13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(17):7532-7549. doi:10.7150/thno.77528 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Signatures of EMT, immunosuppression, and inflammation in primary and recurrent human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma at single-cell resolution
1. Department of Dermatology, Hunan Engineering Research Center of Skin Health and Disease, Hunan Key Laboratory of Skin Cancer and Psoriasis, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
2. National Engineering Research Center of Personalized Diagnostic and Therapeutic Technology, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
3. Department of Urology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
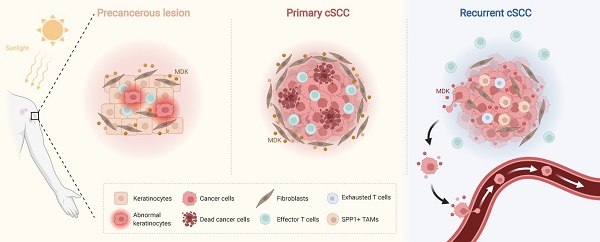
Rationale: The recurrence of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) after surgery is associated with the reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment (TME), and remains a key factor affecting its outcomes.
Methods: We employed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to examine the dynamic changes in epithelial cells, T cells, myeloid cells, and fibroblasts between primary and recurrent cSCC. Cell clustering, cell trajectory, cell-cell communication, and gene set enrichment analysis were used to investigate the TME heterogeneity between primary and recurrent cSCC. Gene expression differences were monitored by IHC staining.
Results: We examined the immunosuppressed microenvironment in recurrent cSCC, which exhibited a T cell-excluded and SPP1+ tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs)-enriched status. In recurrent cSCC, CD8+ T cells showed high exhaustion and low inflammatory features, while SPP1+ TAMs displayed global pro-tumor characteristics, including decreased phagocytosis and inflammation and increased angiogenesis. Furthermore, the subgroups of SPP1+ TAMs harbored distinct functions. SPP1+ CD209high TAMs showed features of phagocytosis, while SPP1+ CD209low TAMs tended to have a high angiogenic ability. A subpopulation of tumor-specific keratinocytes (TSKs) showed significant epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) features in recurrent cSCC, probably due to their active communication with IL7R+ cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). Moreover, we found that the pleiotropic growth factor/cytokine Midkine (MDK) could provoke different cell-cell interactions in cSCC with distinctive staging. In primary cSCC, MDK was highly expressed in fibroblasts and could promote their proliferation and block the migration of tumor cells, while in recurrent cSCC, the high expression of MDK in TSKs promoted their proliferation and metastasis.
Conclusion: Our study provides insights into the critical mechanisms of cSCC progression, which might facilitate the development of a powerful approach for the prevention and treatment of cSCC recurrence.
Keywords: cSCC, recurrence, TME, EMT, immunosuppression, inflammation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact