13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(7):2656-2674. doi:10.7150/thno.91456 This issue Cite
Research Paper
AXL-specific single domain antibodies show diagnostic potential and anti-tumor activity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
1. Translational Oncology Research Center (TORC), team Hematology and Immunology (HEIM), Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium.
2. Laboratory of Dendritic Cell Biology and Cancer Immunotherapy, VIB Center for Inflammation Research, Brussels, Belgium.
3. Brussels Center of Immunology, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium.
4. Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Therapy (MITH), Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium.
5. Department of Hematology, Ghent University Hospital, Ghent, Belgium.
6. Translational Oncology Research Center (TORC), team Hematology and Immunology (HEIM), Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel, Brussels, Belgium.
7. Translational Oncology Research Center (TORC), Laboratory for Molecular and Cellular Therapy (LMCT), Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium.
* Authors equally contributed.
Abstract
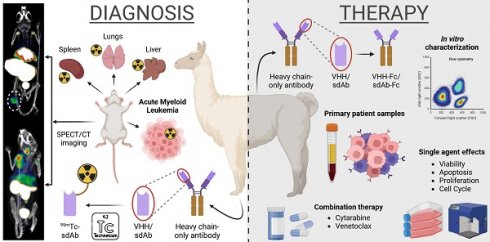
Rationale: AXL expression has been identified as a prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and is detectable in approximately 50% of AML patients. In this study, we developed AXL-specific single domain antibodies (sdAbs), cross-reactive for both mouse and human AXL protein, to non-invasively image and treat AXL-expressing cancer cells.
Methods: AXL-specific sdAbs were induced by immunizing an alpaca with mouse and human AXL proteins. SdAbs were characterized using ELISA, flow cytometry, surface plasmon resonance and the AlphaFold2 software. A lead compound was selected and labeled with 99mTc for evaluation as a diagnostic tool in mouse models of human (THP-1 cells) or mouse (C1498 cells) AML using SPECT/CT imaging. For therapeutic purposes, the lead compound was fused to a mouse IgG2a-Fc tail and in vitro functionality tests were performed including viability, apoptosis and proliferation assays in human AML cell lines and primary patient samples. Using these in vitro models, its anti-tumor effect was evaluated as a single agent, and in combination with standard of care agents venetoclax or cytarabine.
Results: Based on its cell binding potential, cross-reactivity, nanomolar affinity and GAS6/AXL blocking capacity, we selected sdAb20 for further evaluation. Using SPECT/CT imaging, we observed tumor uptake of 99mTc-sdAb20 in mice with AXL-positive THP-1 or C1498 tumors. In THP-1 xenografts, an optimized protocol using pre-injection of cold sdAb20-Fc was required to maximize the tumor-to-background signal. Besides its diagnostic value, we observed a significant reduction in tumor cell proliferation and viability using sdAb20-Fc in vitro. Moreover, combining sdAb20-Fc and cytarabine synergistically induced apoptosis in human AML cell lines, while these effects were less clear when combined with venetoclax.
Conclusions: Because of their diagnostic potential, sdAbs could be used to screen patients eligible for AXL-targeted therapy and to follow-up AXL expression during treatment and disease progression. When fused to an Fc-domain, sdAbs acquire additional therapeutic properties that can lead to a multidrug approach for the treatment of AXL-positive cancer patients.
Keywords: single domain antibodies, AXL, nuclear imaging, therapy, acute myeloid leukemia
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact