13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(3):1076-1090. doi:10.7150/thno.79434 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hepatic PTP4A1 ameliorates high-fat diet-induced hepatosteatosis and hyperglycemia by the activation of the CREBH/FGF21 axis
1. Biotherapeutics Translational Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience & Biotechnology (KRIBB), 125 Gwahak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34141, Republic of Korea.
2. Metabolic Regulation Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience & Biotechnology (KRIBB), 125 Gwahak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34141, Republic of Korea.
3. Laboratory Animal Resource Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience & Biotechnology (KRIBB), 125 Gwahak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34141, Republic of Korea.
4. Department of Bioscience, KRIBB School of Bioscience, Korea University of Science and Technology (UST), 125 Gwahak-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon 34141, Republic of Korea.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
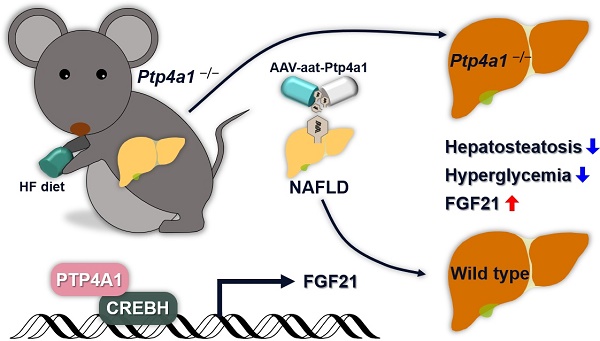
Precise regulation of kinases and phosphatases is crucial for human metabolic homeostasis. This study aimed to investigate the roles and molecular mechanisms of protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA1 (PTP4A1) in regulating hepatosteatosis and glucose homeostasis.
Method: Ptp4a1-/- mice, adeno-associated virus encoding Ptp4a1 under liver-specific promoter, adenovirus encoding Fgf21, and primary hepatocytes were used to evaluate PTP4A1-mediated regulation in the hepatosteatosis and glucose homeostasis. Glucose tolerance test, insulin tolerance test, 2-deoxyglucose uptake assay, and hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp were performed to estimate glucose homeostasis in mice. The staining, including oil red O, hematoxylin & eosin, and BODIPY, and biochemical analysis for hepatic triglycerides were performed to assess hepatic lipids. Luciferase reporter assays, immunoprecipitation, immunoblots, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and immunohistochemistry staining were conducted to explore the underlying mechanism.
Results: Here, we found that deficiency of PTP4A1 aggravated glucose homeostasis and hepatosteatosis in mice fed a high-fat (HF) diet. Increased lipid accumulation in hepatocytes of Ptp4a1-/- mice reduced the level of glucose transporter 2 on the plasma membrane of hepatocytes leading to a diminution of glucose uptake. PTP4A1 prevented hepatosteatosis by activating the transcription factor cyclic adenosine monophosphate-responsive element-binding protein H (CREBH)/fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) axis. Liver-specific PTP4A1 or systemic FGF21 overexpression in Ptp4a1-/- mice fed an HF diet restored the disorder of hepatosteatosis and glucose homeostasis. Finally, liver-specific PTP4A1 expression ameliorated an HF diet-induced hepatosteatosis and hyperglycemia in wild-type mice.
Conclusions: Hepatic PTP4A1 is critical for regulating hepatosteatosis and glucose homeostasis by activating the CREBH/FGF21 axis. Our current study provides a novel function of PTP4A1 in metabolic disorders; hence, modulating PTP4A1 may be a potential therapeutic strategy against hepatosteatosis-related diseases.
Keywords: PTP4A1, hepatosteatosis, glucose homeostasis, CREBH, FGF21
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact