13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(9):4237-4249. doi:10.7150/thno.69035 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Extracellular vesicle-derived miR-144 as a novel mechanism for chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced endothelial dysfunction
1. Beijing An Zhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing Institute of Heart Lung and Blood Vessel Disease, Beijing, 100029, China.
2. Department of Biomedical Scienecs, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 508057, China.
3. Department of Emergency Medicine, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pa, PA19107, USA.
4. Department of Emergency, Beijing An Zhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100029, China.
5. Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Capital Institute of Pediatrics, Beijing, 100020, China.
Abstract
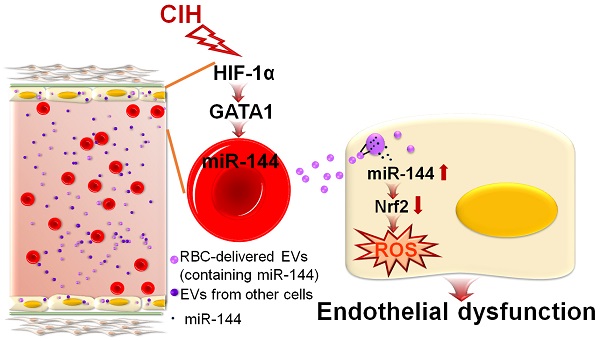
Rationale: Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a significant role in cell-cell communication. However, whether and how extracellular vesicles are involved in chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced endothelial dysfunction is unknown.
Methods: Comparative transcriptomics analysis and miRNA screening were used to identify the possible pathways or target molecules mediating chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced endothelial function. Serum- or erythrocyte-derived EVs were isolated through ultracentrifugation plus filtration. After in vitro or in vivo treatment with EVs, aortic rings were treated with dihydroethidium staining for superoxidative anion measurement or mounted with wire myography to measure isometric forces. Immunoblotting and qPCR were used for evaluating the molecular mechanism mediating EV miR-144-induced endothelial function under intermittent hypoxia.
Results: We revealed a previously undefined importance of circulating extracellular vesicles in regulating endothelial function via delivery of miR-144 to endothelial cells, reducing nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 expression. Additionally, we identified that erythrocytes were the primary cellular source of miR-144-enriched serum-derived extracellular vesicles and that erythrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles were largely responsible for chronic intermittent hypoxia-impaired endothelial function. Furthermore, silencing of miR-144 by anti-miR-144 confirmed its essential role in endothelial dysfunction elicited by erythrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles from chronic intermittent hypoxia-exposed C57BL/6 mice.
Conclusion: The results expand the scope of blood-borne substances involved in vascular homeostasis and suggest that anti-miR-144-loaded extracellular vesicles may represent a promising therapeutic approach against obstructive sleep apnea or chronic intermittent hypoxia-associated endothelial dysfunction.
Keywords: Chronic intermittent hypoxia, endothelial dysfunction, extracellular vesicle, erythrocyte, miR144-Nrf2 Signaling
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact