13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(5):2133-2149. doi:10.7150/thno.66457 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Rho Kinase regulates neutrophil NET formation that is involved in UVB-induced skin inflammation
1. Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VAMC, Philadelphia, PA, 19104, USA.
2. Department of Dermatology, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 19104, USA.
3. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin 300052, China.
4. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
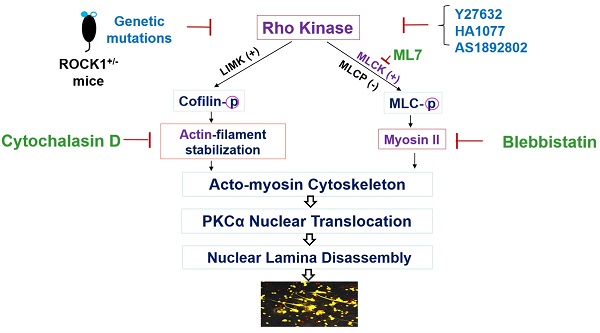
Objective: Ultraviolet B (UVB) is an important trigger of skin inflammation and lupus with leukocyte recruitment to inflamed skin. We recently reported the involvement of neutrophil NETosis in UVB-induced skin inflammation, and that NETotic nuclear envelope rupture is driven by PKCα-mediated nuclear lamin B disassembly. To address the role of Actin cytoskeleton in NETosis, we investigated the effects of Rho kinase (ROCK) and its downstream actomyosin cytoskeletal networks on PKCα nuclear translocation and NET formation, as well as their involvement in UVB-induced skin inflammation.
Methods: We studied the dynamic changes of ROCK and actomyosin cytoskeletal networks during NETosis induction and their involvement in PKCα nuclear translocation. Using mice with hematopoietic-specific ROCK1 deficiency, we investigated the effects of ROCK1 deficiency on NETosis, and its involvement in UVB-induced skin inflammation.
Results: Our time course studies demonstrated the dynamic changes of actin polymerization and ROCK activation, support the role of actin cytoskeleton in nuclear translocation of cytosolic PKCα in early stage of NETosis induction. Inhibition of actin polymerization or key molecules of the ROCK/MLCK/myosin pathway decreased PKCα nuclear translocation and NET formation. Genetic deficiency of ROCK1, inhibited NETosis ex vivo and in vivo, decreased extracellular display of NET-associated IL-17A, TNFα, IFNγ, and IFNα in inflamed skin, which were correlated with the ameliorated skin inflammation in UVB-irradiated mice with hematopoietic-specific ROCK1 deficiency.
Conclusions: ROCK regulated NETosis through modulation of PKCα nuclear translocation via actomyosin cytoskeletal networks in neutrophils. ROCK1 deficiency ameliorated UVB-induced skin inflammation by attenuation of NETosis and NET-associated cytokines.
Keywords: Rho kinase, Neutrophil, NETosis, UVB, Skin inflammation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact