13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(12):5778-5793. doi:10.7150/thno.55946 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Multi-omics study reveals that statin therapy is associated with restoration of gut microbiota homeostasis and improvement in outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome
1. Department of Medical Research Center, State Key Laboratory of Complex Severe and Rare Diseases, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Science & Peking Union Medical College, 100730, Beijing, China.
2. Department of Cardiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Science & Peking Union Medical College, 100730, Beijing, China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Mycology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100101, Beijing, China; Savaid Medical School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100049, Beijing, China.
4. State Key Laboratory of Microbial Resources, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100101, Beijing, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
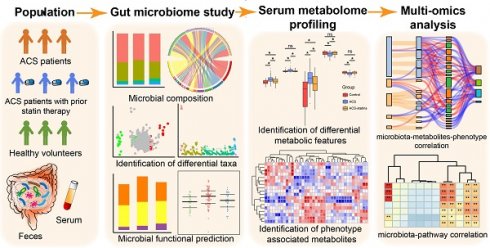
Rationale: Prior chronic treatment with statins has been shown to be associated with more favorable outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Specific changes in the gut microbiota and microbial metabolites have been shown to influence the progression of coronary artery disease. However, the critical microbial and metabolomic changes associated with the cardiovascular protective effects of statins in ACS remain elusive.
Methods: In the present study, we performed 16S rRNA sequencing and serum metabolomic analysis in 36 ACS patients who had received chronic statin treatment, 67 ACS patients who had not, and 30 healthy volunteers. A follow-up study was conducted. Metagenomic functional prediction of important bacterial taxa was achieved using PICRUSt2.
Results: Statins modulated the gut microbiome of ACS patients towards a healthier status, i.e., reducing potentially pathogenic bacteria such as Parabacteroides merdae but increasing beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum, Anaerostipes hadrus and Ruminococcus obeum. Moreover, prior chronic statin therapy was associated with improved outcome in ACS patients. Multi-omics analysis revealed that specific changes in bacterial taxa were associated with disease severity or outcomes either directly or by mediating metabolites such as fatty acids and prenol lipids. Finally, we discovered that important taxa associated with statins were correlated with fatty acid- and isoprenoid-related pathways that were predicted by PICRUSt2.
Conclusions: Our study suggests that statin treatment might benefit ACS patients by modulating the composition and function of the gut microbiome, which might result in improved circulating metabolites and reduced metabolic risk. Our findings provide new insights for understanding the heterogenic roles of statins in ACS patients through host gut microbiota metabolic interactions.
Keywords: statins, acute coronary syndrome, outcome, microbiome, metabolomics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact