13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(21):9741-9766. doi:10.7150/thno.46913 This issue Cite
Review
P21-Activated Kinase 1: Emerging biological functions and potential therapeutic targets in Cancer
1. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Health Science Center, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen, 518060, PR China.
2. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Health Science Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, 518060, PR China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Biotherapy, Chengdu 610041, China.
4. Department of Medicinal Chemistry and Natural Medicine Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, Harbin Medical University, Baojian Road 157, Nangang District, Harbin 150081, PR China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
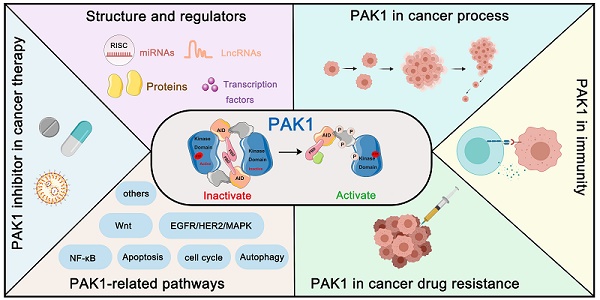
The p21-Activated kinase 1 (PAK1), a member of serine-threonine kinases family, was initially identified as an interactor of the Rho GTPases RAC1 and CDC42, which affect a wide range of processes associated with cell motility, survival, metabolism, cell cycle, proliferation, transformation, stress, inflammation, and gene expression. Recently, the PAK1 has emerged as a potential therapeutic target in cancer due to its role in many oncogenic signaling pathways. Many PAK1 inhibitors have been developed as potential preclinical agents for cancer therapy. Here, we provide an overview of essential roles that PAK1 plays in cancer, including its structure and autoactivation mechanism, its crucial function from onset to progression to metastasis, metabolism, immune escape and even drug resistance in cancer; endogenous regulators; and cancer-related pathways. We also summarize the reported PAK1 small-molecule inhibitors based on their structure types and their potential application in cancer. In addition, we provide overviews on current progress and future challenges of PAK1 in cancer, hoping to provide new ideas for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Keywords: PAK1, structure, cancer, targets, resistance, small molecular inhibitors
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact