13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(16):7351-7368. doi:10.7150/thno.44459 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Protein acetylation derepresses Serotonin Synthesis to potentiate Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function through HDAC1-PKA-Tph1 signaling
1. Shanghai Clinical Center for Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Shanghai Institute of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Department of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200025, China.
2. School of Medicine, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University; Center for Reproductive Medicine, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, 250012, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
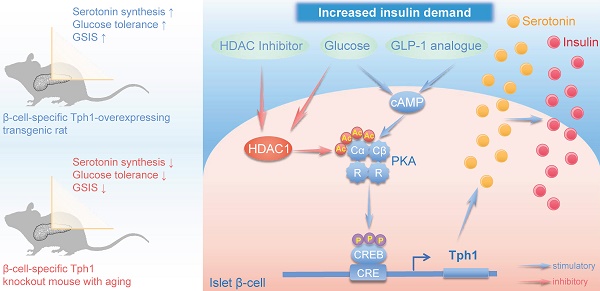
Rationale: Protein acetylation is tightly linked to transcriptional control and energy metabolism. However, the role of protein acetylation in islet function remains enigmatic. This study aims to determine how protein acetylation controls β-cell function and explore the underlying mechanism.
Methods: The gene-expression profiles were analyzed for rat islets in response to two histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. Insulin secretion, tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (Tph1) expression, and serotonin synthesis of rat islets were detected after HDAC inhibitor treatment both in vivo and ex vivo. β-cell-specific Tph1-overexpressing transgenic rats and β-cell-specific Tph1 knockout mice were constructed to evaluate the role of Tph1 in β-cell function. The deacetylation of PKA in β-cells by HDAC1 was investigated by adenoviral infection, immunoprecipitation, and western blot.
Results: Inhibition of HDACs greatly potentiated pancreatic β-cell function and reprogrammed transcriptional landscape of islets. Among the commonly up-regulated genes by two pan-HDAC inhibitors, Tph1 displayed the most prominent change. Specifically, inhibition of HDAC1 and HDAC3 by MS-275 strongly promoted Tph1 expression and endogenous serotonin synthesis in rat islets, concomitantly with enhanced insulin secretory capacity in vivo and ex vivo. β-cell-specific Tph1-overexpressing transgenic rats exhibited improved glucose tolerance and amplified glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. On the contrary, β-cell-specific Tph1 knockout mice displayed glucose intolerance and impaired insulin secretion with aging. Moreover, depletion of Tph1 in β-cells abrogated MS-275-induced insulin hypersecretion. Overexpression of HDAC1, not HDAC3, inhibited Tph1 transcriptional activity and decreased MS-275-stimulated Tph1 expression. Mechanistically, HDAC1 deacetylated PKA catalytic subunit and decreased its activity, resulting in Tph1 transcriptional repression. The acetylation mimetic K62Q mutant of PKA increased its catalytic activity. HDAC1 inhibition exerted a synergistic effect with cAMP/PKA signal on Tph1 expression.
Conclusions: The present findings highlight a novel role of HDAC1-PKA-Tph1 signaling in governing β-cell functional compensation by derepressing serotonin synthesis.
Keywords: Protein acetylation, Beta-cell function, Serotonin, Tph1, PKA, HDAC1
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact