13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(14):6430-6447. doi:10.7150/thno.43177 This issue Cite
Research Paper
In vivo imaging of Zika virus reveals dynamics of viral invasion in immune-sheltered tissues and vertical propagation during pregnancy
1. CAS Key Laboratory of Special Pathogens and Biosafety, Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China
2. Center for Brain Science, State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance in Biological Systems, Wuhan Center for Magnetic Resonance, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China
3. College of Life Sciences and Food Engineering, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan 056038, China
4. State Key Laboratory of Virology, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China
5. Institute for Infection and Immunity, St George's, University of London, London, SW17 0RE, UK
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
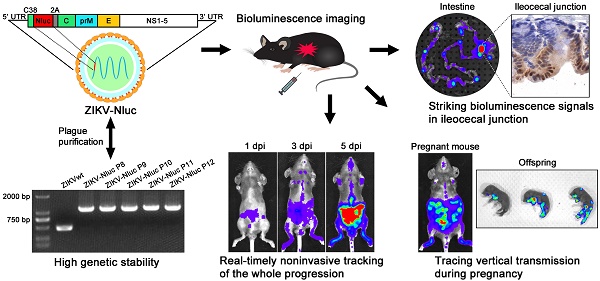
Rationale: Zika virus (ZIKV) is a pathogenic virus known to cause a wide range of congenital abnormalities, including microcephaly, Guillain-Barre syndrome, meningoencephalitis, and other neurological complications, in humans. This study investigated the noninvasive detection of ZIKV infection in vivo, which is necessary for elucidating the virus's mechanisms of viral replication and pathogenesis, as well as to accelerate the development of anti-ZIKV therapeutic strategies.
Methods: In this study, a recombinant ZIKV harbouring Nluc gene (ZIKV-Nluc) was designed, recovered, and purified. The levels of bioluminescence were directly correlated with viral loads in vitro and in vivo. The dynamics of ZIKV infection in A129 (interferon (IFN)-α/β receptor deficient), AG6 (IFN-α/β and IFN-γ receptor deficient), and C57BL/6 mice were characterized. Pregnant dams were infected with ZIKV-Nluc at E10 via intra footpad injection. Then, the pooled immune sera (anti-ZIKV neutralizing antibodies) #22-1 in ZIKV-Nluc virus-infected mice were visualized.
Results: ZIKV-Nluc showed a high genetic stability and replicated well in cells with similar properties to the wild-type ZIKV (ZIKVwt). Striking bioluminescence signals were consistently observed in animal organs, including spleen, intestine, testis, uterus/ovary, and kidney. The ileocecal junction was found to be the crucial visceral target. Infection of pregnant dams with ZIKV-Nluc showed that ZIKV was capable of crossing the maternal-fetal barrier to infect the fetuses via vertical transmission. Furthermore, it was visualized that treatment with the pooled immune sera was found to greatly restrict the spread of the ZIKV-Nluc virus in mice.
Conclusions: This study is the first to report the real-time noninvasive tracking of the progression of ZIKV invading immune-sheltered tissues and propagating vertically during pregnancy. The results demonstrate that ZIKV-Nluc represents a powerful tool for the study of the replication, dissemination, pathogenesis, and treatment of ZIKV in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: Zika virus, Bioluminescence imaging, Viscera dissemination, Tissue localization, Vertical transmission, Pooled immune sera
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact