13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(14):6201-6215. doi:10.7150/thno.46137 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CDK12 and PAK2 as novel therapeutic targets for human gastric cancer
1. Department of Pathophysiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Academy of Medical Science, College of Medicine, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450001, China.
2. China-US (Henan) Hormel Cancer Institute, No.127, Dongming Road, Jinshui District, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450008, China
3. Department of Digestive, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan Cancer Hospital, No.127, Dongming Road, Jinshui District, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450008, China.
4. The Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, Austin, MN 55912, USA.
5. Department of Food and Nutrition, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 52828, Republic of Korea
Abstract
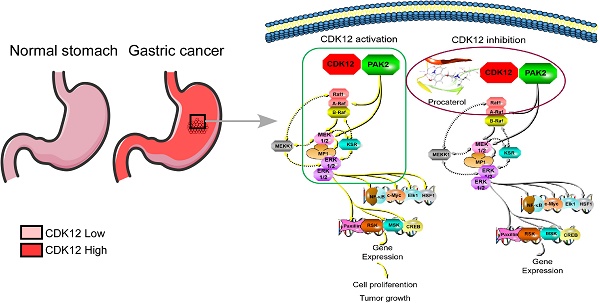
Background: Gastric cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related death, and the third in mortality due to lack of effective therapeutic targets for late stage cancer patients. This study aims to identify potential druggable target biomarkers as potential therapeutic options for patients with gastric cancer.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry of human gastric tumor tissues was conducted to determine the expression level of cyclin-dependent kinase 12 (CDK12). Multiple in vitro and in vivo assays such as RNAi, mass spectrometry, computer docking models, kinase assays, cell xenograft NU/NU mouse models (CDXs) and patient-derived xenograft NOD/SCID mouse models (PDXs) were conducted to study the function and molecular interaction of CDK12 with p21 activated kinase 2 (PAK2), as well as to find CDK12 inhibitors as potential treatment options for human gastric cancer.
Results: Here we identified that CDK12 is a driver gene in human gastric cancer growth. Mechanistically, CDK12 directly binds to and phosphorylates PAK2 at T134/T169 to activate MAPK signaling pathway. We further identified FDA approved clinical drug procaterol can serve as an effective CDK12 inhibitor, leading to dramatic restriction of cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth in human gastric cancer cells and PDXs.
Conclusions: Our data highlight the potential of CDK12/PAK2 as therapeutic targets for patients with gastric cancer, and we propose procaterol treatment as a novel therapeutic strategy for human gastric cancer.
Keywords: gastric cancer, CDK12, PAK2, phosphorylation, procaterol
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact