13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(20):6019-6030. doi:10.7150/thno.35747 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MTBP regulates cell survival and therapeutic sensitivity in TP53 wildtype glioblastomas
1. Department of Neurosurgery, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China
2. Department of Pathology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China
3. Department of Neurosurgery, Shanghai First People's Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200080, China
4. Department of Radiotherapy, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
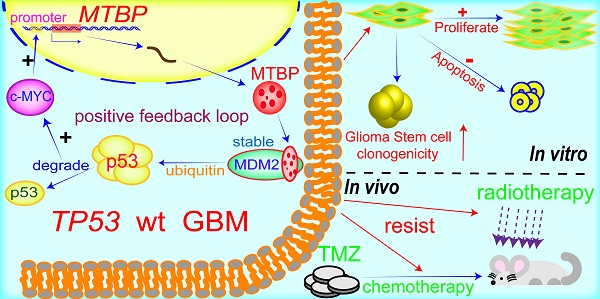
Background: Glioblastoma (GBM) is highly proliferative and resistant to radio-chemotherapy. Loss of tumor suppressor gene TP53 function frequently occurs at protein level in GBMs. This inhibition is often mediated by other components within the p53 signaling axis, including MDM2, whose binding protein (MTBP) plays an important role in the regulation of MDM2 and p53 activity. We investigated the role of MTBP in the biology of TP53-wildtype (TP53wt) GBMs.
Methods: MTBP expression was examined in TCGA and REMBRANDT datasets. MTBP was silenced or overexpressed in TP53wt GBM cells and glioma stem cells (GSCs). The effects on cell viability, apoptosis, and clonogenicity were assessed. The transcriptional regulation of MTBP was investigated.
Results: Upregulation of MTBP was correlated with the Classical molecular subtype, and it predicted poor survival. In TP53wt GBM cells, the protein levels of MTBP were positively associated with those of MDM2 but negatively correlated with those of p53. MTBP knockdown promoted apoptosis and inhibited clonogenicity, while overexpression of this protein enhanced tumorigenicity in vitro and in vivo. The pro-survival effect of MTBP depended on the activity of MDM2 and p53. MTBP was transcriptionally regulated by c-myc, thereby forming a positive regulatory loop. Finally, MTBP silencing increased the sensitivity of TP53wt GSCs to radiation and TMZ treatment in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: MTBP regulates the cell survival and treatment sensitivity of TP53wt GBMs through MDM2-dependent post-translational modification of p53. MTBP-targeting treatments are potentially useful in increasing patients' survival.
Keywords: Glioma, MTBP, MDM2, p53, apoptosis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact