13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(7):2993-3013. doi:10.7150/thno.97320 This issue Cite
Review
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Cancer: A Revisited Review from Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies
1. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Breast Surgery, Department of Outpatient, and Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, China.
2. Sichuan Engineering Research Center for Biomimetic Synthesis of Natural Drugs, School of Life Science and Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China.
#These authors made equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
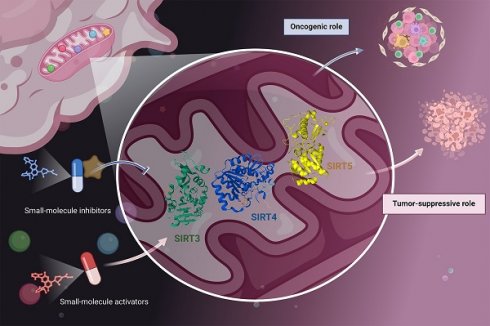
The sirtuin (SIRT) family is well-known as a group of deacetylase enzymes that rely on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Among them, mitochondrial SIRTs (SIRT3, SIRT4, and SIRT5) are deacetylases located in mitochondria that regulate the acetylation levels of several key proteins to maintain mitochondrial function and redox homeostasis. Mitochondrial SIRTs are reported to have the Janus role in tumorigenesis, either tumor suppressive or oncogenic functions. Although the multi-faceted roles of mitochondrial SIRTs with tumor-type specificity in tumorigenesis, their critical functions have aroused a rising interest in discovering some small-molecule compounds, including inhibitors and activators for cancer therapy. Herein, we describe the molecular structures of mitochondrial SIRTs, focusing on elucidating their regulatory mechanisms in carcinogenesis, and further discuss the recent advances in developing their targeted small-molecule compounds for cancer therapy. Together, these findings provide a comprehensive understanding of the crucial roles of mitochondrial SIRTs in cancer and potential new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Mitochondrial sirtuin, Cancer therapy, Small-molecule compound, SIRT3, SIRT4, SIRT5
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact