13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(2):662-680. doi:10.7150/thno.87344 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Microenvironment-induced CREPT expression by cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles primes field cancerization
1. State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, School of Medicine, National Engineering Laboratory for Anti-tumor Therapeutics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.
2. Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences, School of Medicine, School of Life Science, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.
3. Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of PLA, Beijing 100700, China.
4. State Key Laboratory of Protein and Plant Gene Research, School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China.
5. Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center and Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Shanghai Medical College, Key Laboratory of Breast Cancer in Shanghai, Innovation Center for Cell Signaling Network, Cancer Institutes, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
6. Department of Pathology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, 2-2 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871, Japan.
7. Institute of Pathology, Medical University of Innsbruck, A-6020 Innsbruck, Austria.
8. Department of Oncology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200080, China.
# These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
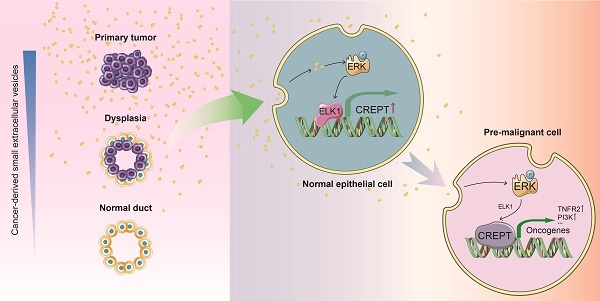
Rationale: Cancer local recurrence increases the mortality of patients, and might be caused by field cancerization, a pre-malignant alteration of normal epithelial cells. It has been suggested that cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles (CDEs) may contribute to field cancerization, but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. In this study, we aim to identify the key regulatory factors within recipient cells under the instigation of CDEs.
Methods: In vitro experiments were performed to demonstrate that CDEs promote the expression of CREPT in normal epithelial cells. TMT-based quantitative mass spectrometry was employed to investigate the proteomic differences between normal cells and tumor cells. Loss-of-function approaches by CRISPR-Cas9 system were used to assess the role of CREPT in CDEs-induced field cancerization. RNA-seq was performed to explore the genes regulated by CREPT during field cancerization.
Results: CDEs promote field cancerization by inducing the expression of CREPT in non-malignant epithelial cells through activating the ERK signaling pathway. Intriguingly, CDEs failed to induce field cancerization when CREPT was deleted, highlighting the importance of CREPT. Transcriptomic analyses revealed that CDEs elicited inflammatory responses, primarily through activation of the TNF signaling pathway. CREPT, in turn, regulates the transduction of downstream signals of TNF by modulating the expression of TNFR2 and PI3K, thereby promoting inflammation-to-cancer transition.
Conclusion: CREPT not only serves as a biomarker for field cancerization, but also emerges as a target for preventing the cancer local recurrence.
Keywords: cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles, field cancerization, CREPT
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact