13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(12):4247-4265. doi:10.7150/thno.86528 This issue Cite
Review
Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic implications of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins, the emerging crucial m6A regulators of tumors
1. Department of Surgical Oncology and General Surgery, Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Tumors, Ministry of Education, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning 110001, People's Republic of China.
2. Department of Anesthesiology, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning 110001, People's Republic of China.
3. Department of Plastic Surgery, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning 110001, People's Republic of China.
4. Department of Endoscopy, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning 110001, People's Republic of China.
5. Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning 110001, People's Republic of China.
6. Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, China Medical University, Shenyang, 110122, People's Republic of China.
7. Liaoning Key Laboratory of Molecular Targeted Anti-Tumor Drug Development and Evaluation; Liaoning Cancer Immune Peptide Drug Engineering Technology Research Center; Key Laboratory of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Tumors, Ministry of Education; China Medical University, Shenyang, 110122, People's Republic of China.
8. Shenyang Kangwei Medical Laboratory Analysis Co. LTD, Liaoning Province, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work: Heng Zhou, Qiang Sun, Mingliang Feng.
Abstract
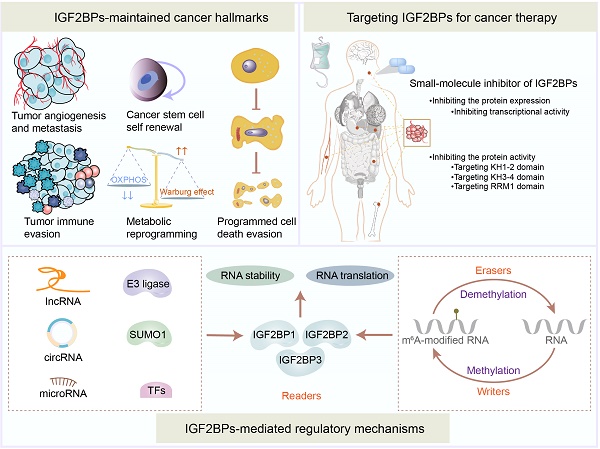
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs) serve essential biological functions as post-transcriptional performers, participating in the acquisition or maintenance of tumor hallmarks due to their distinct protein structures. Emerging evidence indicates that IGF2BPs belong to the class III type of RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification readers, controlling RNA stability, storage, localization, metabolism, and translation in multiple vital bioprocesses, particularly tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Here, we discuss the underlying regulatory mechanisms and pathological functions of IGF2BPs which act as m6A readers in the context of tumor pathogenesis and multidrug resistance. Furthermore, we highlight the potential of IGF2BPs as drug targets in clinical tumor treatment. Hence, precise and novel tumor therapeutic approaches could be uncovered by targeting epigenetic heterogeneity.
Keywords: Cancer, N6-methyladenosine, IGF2BPs, Reader, Cancer therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact