13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(6):1921-1948. doi:10.7150/thno.81656 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The lysophosphatidic acid-regulated signal transduction network in ovarian cancer cells and its role in actomyosin dynamics, cell migration and entosis
1. Department of Translational Oncology, Center for Tumor Biology and Immunology, Philipps University, Marburg, Germany
2. Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry, Max-Planck-Institute for Heart and Lung Research, Bad Nauheim, Germany
3. Genomics Core Facility, Philipps University, Marburg, Germany
4. Bioinformatics Core Facility, Philipps University, Marburg, Germany
5. Institut for Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology, Albert-Ludwigs University, Freiburg, Germany
6. Institute for Translational Proteomics, Philipps University, Marburg, Germany
Abstract
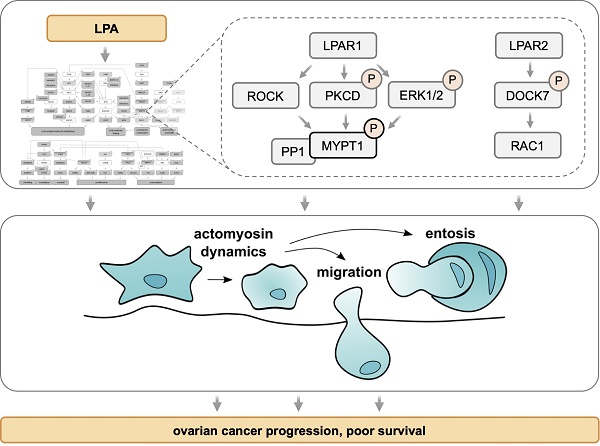
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) species accumulate in the ascites of ovarian high-grade serous cancer (HGSC) and are associated with short relapse-free survival. LPA is known to support metastatic spread of cancer cells by activating a multitude of signaling pathways via G-protein-coupled receptors of the LPAR family. Systematic unbiased analyses of the LPA-regulated signal transduction network in ovarian cancer cells have, however, not been reported to date.
Methods: LPA-induced signaling pathways were identified by phosphoproteomics of both patient-derived and OVCAR8 cells, RNA sequencing, measurements of intracellular Ca2+ and cAMP as well as cell imaging. The function of LPARs and downstream signaling components in migration and entosis were analyzed by selective pharmacological inhibitors and RNA interference.
Results: Phosphoproteomic analyses identified > 1100 LPA-regulated sites in > 800 proteins and revealed interconnected LPAR1, ROCK/RAC, PKC/D and ERK pathways to play a prominent role within a comprehensive signaling network. These pathways regulate essential processes, including transcriptional responses, actomyosin dynamics, cell migration and entosis. A critical component of this signaling network is MYPT1, a stimulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), which in turn is a negative regulator of myosin light chain 2 (MLC2). LPA induces phosphorylation of MYPT1 through ROCK (T853) and PKC/ERK (S507), which is majorly driven by LPAR1. Inhibition of MYPT1, PKC or ERK impedes both LPA-induced cell migration and entosis, while interference with ROCK activity and MLC2 phosphorylation selectively blocks entosis, suggesting that MYPT1 figures in both ROCK/MLC2-dependent and -independent pathways. We finally show a novel pathway governed by LPAR2 and the RAC-GEF DOCK7 to be indispensable for the induction of entosis.
Conclusion: We have identified a comprehensive LPA-induced signal transduction network controlling LPA-triggered cytoskeletal changes, cell migration and entosis in HGSC cells. Due to its pivotal role in this network, MYPT1 may represent a promising target for interfering with specific functions of PP1 essential for HGSC progression.
Keywords: entosis, migration, lysophosphatidic acid, DOCK7, MYPT1
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact