13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(2):596-610. doi:10.7150/thno.78687 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Enhancer RNA promotes resistance to radiotherapy in bone-metastatic prostate cancer by m6A modification
1. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Molecular Nuclear Medicine, Institute of Radiation Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Tianjin, 300192, China
2. Department of Urology, The Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, 300211, China
3. Department of Urology, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200127, China
4. Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin, 300192, China
5. Department of Urology, Shanghai Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China
6. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 55905, USA
#These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
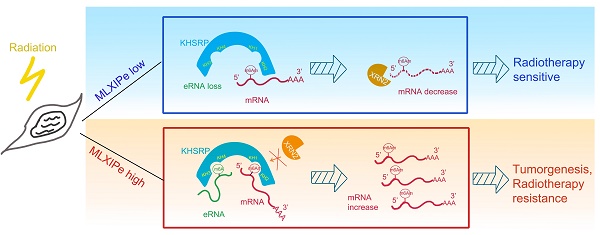
Rationale: Prostate cancer metastasizes to the bone with the highest frequency and exhibits high resistance to 177Lu-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) radioligand therapy. Little is known about bone metastatic prostate cancer (mPCa) resistance to radiation.
Methods: We filtered the metastatic eRNA using RNA-seq, MeRIP-seq, RT-qPCR and bioinformation. Western blot, RT-qPCR, CLIP, co-IP and RNA pull-down assays were used for RNA/protein interaction, RNA or protein expression examination. MTS assay was used to determine cell viability in vitro, xenograft assay was used to examine the tumor growth in mice.
Results: In this study, we screened and identified bone-specific N6 adenosine methylation (m6A) on enhancer RNA (eRNA) that played a post-transcriptional functional role in bone mPCa and was correlated with radiotherapy (RT) resistance. Further data demonstrated that RNA-binding protein KHSRP recognized both m6A at eRNA and m6Am at 5'-UTR of mRNA to block RNA degradation from exoribonuclease XRN2. Depletion of the MLXIPe/KHSRP/PSMD9 regulatory complex inhibited tumor growth and RT sensitization of bone mPCa xenograft in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that a bone-specific m6A-modified eRNA plays a vital role in regulating mPCa progression and RT resistance and might be a novel specific predictor for cancer RT.
Keywords: Bone metastatic prostate cancer, m6A, Enhancer RNA, m6Am, Radiotherapy.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact