13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(1):231-249. doi:10.7150/thno.78878 This issue Cite
Research Paper
SIRT6-regulated macrophage efferocytosis epigenetically controls inflammation resolution of diabetic periodontitis
1. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China.
2. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Stomatology, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China.
3. Department of Basic Science of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Stomatology, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China.
4. Jiangsu Province Engineering Research Center of Stomatological Translational Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
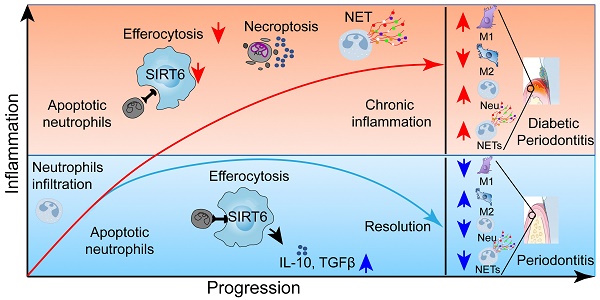
Rationale: Diabetes exacerbates the prevalence and severity of periodontitis, leading to severe periodontal destruction and ultimately tooth loss. Delayed resolution of inflammation is a major contributor to diabetic periodontitis (DP) pathogenesis, but the underlying mechanisms of this imbalanced immune homeostasis remain unclear.
Methods: We collected periodontium from periodontitis with or without diabetes to confirm the dysfunctional neutrophils and macrophages in aggravated inflammatory damage and impaired inflammation resolution. Our in vitro experiments confirmed that SIRT6 inhibited macrophage efferocytosis by restraining miR-216a-5p-216b-5p-217 cluster maturation through ''non-canonical'' microprocessor complex (RNA pulldown, RIP, immunostaining, CHIP, Luciferase assays, and FISH). Moreover, we constructed m6SKO mice that underwent LIP-induced periodontitis to explore the in vitro and in vivo effect of SIRT6 on macrophage efferocytosis. Finally, antagomiR-217, a miRNA antagonism, was delivered into the periodontium to treat LIP-induced diabetic periodontitis.
Results: We discovered that insufficient SIRT6 as a histone deacetylase in macrophages led to unresolved inflammation and aggravated periodontitis in both human and mouse DP with accumulated apoptotic neutrophil (AN) and higher generation of neutrophil extracellular traps. Mechanistically, we validated that macrophage underwent high glucose stimulation resulting in disturbance of the SIRT6-miR-216/217 axis that triggered impeded efferocytosis of AN through targeting the DEL-1/CD36 axis directly. Furthermore, we demonstrated the inhibitory role of SIRT6 for MIR217HG transcription and identified a non-canonical action of microprocessor that SIRT6 epigenetically hindered the splicing of the primary miR-216/217 via the complex of hnRNPA2B1, DGCR8, and Drosha. Notably, by constructing myeloid-specific deletion of SIRT6 mice and locally delivering antagomir-217 in DP models, we strengthened the in vivo effect of this axis in regulating macrophage efferocytosis and inflammation resolution in DP.
Conclusions: Our findings delineated the emerging role of SIRT6 in mediating metabolic dysfunction-associated inflammation, and therapeutically targeting this regulatory axis might be a promising strategy for treating diabetes-associated inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: SIRT6, Macrophage efferocytosis, Neutrophil extracellular trap, Inflammation resolution, Diabetes, Periodontitis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact