13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(1):20-39. doi:10.7150/thno.76894 This issue Cite
Review
Engineered biomembrane-derived nanoparticles for nanoscale theranostics
1. Institute of Translational Medicine, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China.
2. Institute of Medicine, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China.
3. Musculoskeletal Organoid Research Center, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China.
4. Department of Trauma Orthopedics, Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, 200433, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
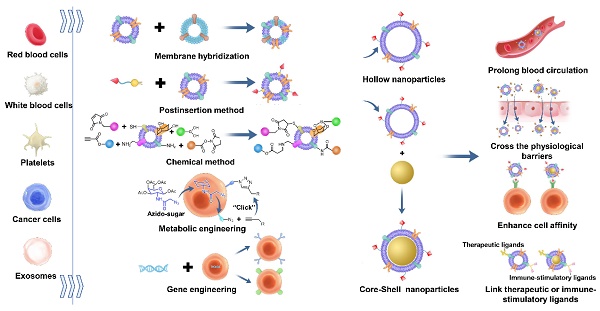
Currently, biological membrane-derived nanoparticles (NPs) have shown enormous potential as drug delivery vehicles due to their outstanding biomimetic properties. To make these NPs more adaptive to complex biological systems, some methods have been developed to modify biomembranes and endow them with more functions while preserving their inherent natures. In this review, we introduce five common approaches used for biomembrane decoration: membrane hybridization, the postinsertion method, chemical methods, metabolism engineering and gene engineering. These methods can functionalize a series of biomembranes derived from red blood cells, white blood cells, tumor cells, platelets, exosomes and so on. Biomembrane engineering could markedly facilitate the targeted drug delivery, treatment and diagnosis of cancer, inflammation, immunological diseases, bone diseases and Alzheimer's disease. It is anticipated that these membrane modification techniques will advance biomembrane-derived NPs into broader applications in the future.
Keywords: biomembrane-derived nanoparticles, biomimetic, biomembrane engineering, targeted drug delivery, nanoscale theranostics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact