13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(1):1-15. doi:10.7150/thno.73966 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Polymeric microneedles enable simultaneous delivery of cancer immunomodulatory drugs and detection of skin biomarkers
1. Institute for Medical Engineering and Science (IMES), Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139.
2. Department of Medicine, Division of Engineering in Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115.
3. Center for Systems Biology, Massachusetts General Hospital Research Institute, Boston, MA 02114.
4. Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114.
5. Department of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School.
6. Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, Harvard University, Boston, MA, 02115.
* co-first authors.
Abstract
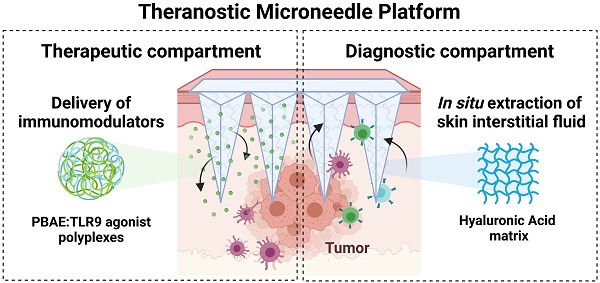
Background: Immune-modulating therapies impart positive outcomes in a subpopulation of cancer patients. Improved delivery strategies and non-invasive monitoring of anti-tumor effects can help enhance those outcomes and understand the mechanisms associated with the generation of anti-tumor immune responses following immunotherapy.
Methods: We report on the design of a microneedle (MN) platform capable of simultaneous delivery of immune activators and collection of interstitial skin fluid (ISF) to monitor therapeutic responses. While either approach has shown promise, the integration of the therapy and diagnostic arms into one MN platform has hardly been explored before. MNs were synthesized out of crosslinked hyaluronic acid (HA) and loaded with a model immunomodulatory nanoparticle-containing drug, CpG oligodinucleotides (TLR9 agonist), for cancer therapy in melanoma and colon cancer models. The therapeutic response was monitored by longitudinal analysis of entrapped immune cells in the MNs following patch retrieval and digestion.
Results: Transdermal delivery of CpG-containing NPs with MNs induced anti-tumor immune responses in multiple syngeneic mouse cancer models. CpG-loaded MNs stimulated innate immune cells and reduced tumor growth. Intravital microscopy showed deposition and spatiotemporal co-localization of CpG-NPs within the tumor microenvironment when delivered with MNs. Analysis of MN-sampled ISF revealed similar immune signatures to those seen in the bulk tumor homogenate, such as increased populations of macrophages and effector T cells following treatment.
Conclusions: Our hydrogel-based MNs enable effective transdermal drug delivery into immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, and upon retrieval, enable studying the immune response to the therapy over time. This platform has the theranostic potential to deliver a range of combination therapies while detecting biomarkers.
Keywords: microneedles, immunotherapy, cancer, poly(beta-amino ester)s, theranostics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact