13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(16):6955-6971. doi:10.7150/thno.77256 This issue Cite
Review
Extracellular vesicles: catching the light of intercellular communication in fibrotic liver diseases
1. School of Life Sciences, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, 100029, China.
2. School of Chinese Materia Medica, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, 100029, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
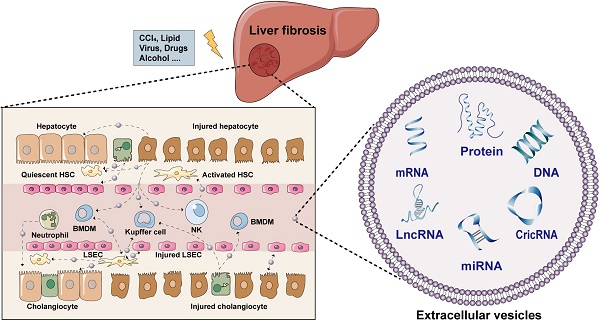
The increasing prevalence of fibrotic liver diseases resulting from different etiologies has become a major global problem for public health. Fibrotic liver diseases represent a redundant accumulation of extracellular matrix, dysregulation of immune homeostasis and angiogenesis, which eventually contribute to the progression of cirrhosis and liver malignancies. The concerted actions among liver cells including hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells, kupffer cells, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and other immune cells are essential for the outcome of liver fibrosis. Recently, a growing body of literature has highlighted that extracellular vesicles (EVs) are critical mediators of intercellular communication among different liver cells either in local or distant microenvironments, coordinating a variety of systemic pathological and physiological processes. Despite the increasing interests in this field, there are still relatively few studies to classify the contents and functions of EVs in intercellular transmission during hepatic fibrogenesis. This review aims to summarize the latest findings with regards to the cargo loading, release, and uptake of EVs in different liver cells and clarify the significant roles of EVs played in fibrotic liver diseases.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles, fibrotic liver disease, intercellular communication, hepatocyte, hepatic stellate cell
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact