13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(14):6291-6307. doi:10.7150/thno.71456 This issue Cite
Research Paper
m6A-induced lncDBET promotes the malignant progression of bladder cancer through FABP5-mediated lipid metabolism
1. Department of Urology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, PR China.
2. National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, PR China.
*These authors are joint senior authors.
Abstract
The limited effect of adjuvant therapy for advanced bladder cancer (BCa) leads to a poor prognosis. Increasing evidence has shown that RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification plays important functional roles in tumorigenesis. Nevertheless, the role and mechanism of m6A-modified noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) in BCa remain largely unknown.
Methods: RT-PCR, western blotting and ONCOMINE dataset were used to determine the dominant m6A-related enzyme in BCa. M6A-lncRNA epitranscriptomic microarray was used to screen candidate targets of METTL14. RT-PCR, MeRIP and TCGA dataset were carried out to confirm the downstream target of METTL14. CHIRP/MS was conducted to identify the candidate proteins binding to lncDBET. RT-PCR, western blotting, RIP and KEGG analysis were used to confirm the target of lncDBET. The levels of METTL14, lncDBET and FABP5 were tested in vitro and in vivo. CCK-8, EdU, transwell and flow cytometry assays were performed to determine the oncogenic function of METTL14, lncDBET and FABP5, and their regulatory networks.
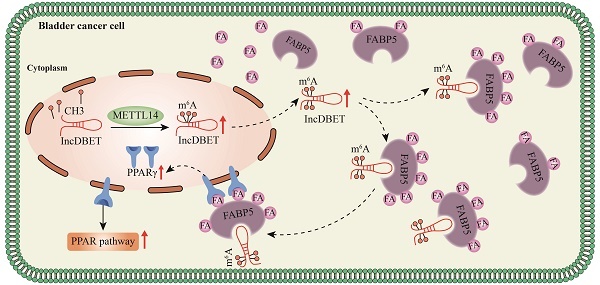
Results: We identified that the m6A level of total RNA was elevated and that METTL14 was the dominant m6A-related enzyme in BCa. m6A modification mediated by METTL14 promoted the malignant progression of BCa by promoting the expression of lncDBET. Upregulated lncDBET activated the PPAR signalling pathway to promote the lipid metabolism of cancer cells through direct interaction with FABP5, thus promoting the malignant progression of BCa in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: Our study establishes METTL14/lncDBET/FABP5 as a critical oncogenic axis in BCa.
Keywords: Bladder cancer, m6A, METTL14, lncDBET, FABP5
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact