13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(14):6273-6290. doi:10.7150/thno.76854 This issue Cite
Review
Immunosuppression in tumor immune microenvironment and its optimization from CAR-T cell therapy
1. Department of Interventional Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450052, China
2. Interventional Institute of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450052, China
3. Interventional Treatment and Clinical Research Center of Henan Province, Zhengzhou, Henan 450052, China
4. Department of Pediatric Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450052, China
5. Department of Colorectal Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450052, China
6. Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan 450052, China
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Abstract
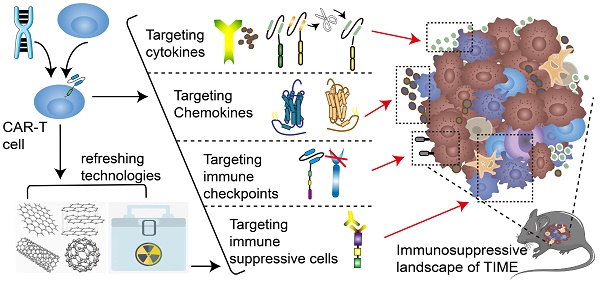
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy represents a landmark advance in personalized cancer treatment. CAR-T strategy generally engineers T cells from a specific patient with a new antigen-specificity, which has achieved considerable success in hematological malignancies, but scarce benefits in solid tumors. Recent studies have demonstrated that tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) cast a profound impact on the immunotherapeutic response. The immunosuppressive landscape of TIME is a critical obstacle to the effector activity of CAR-T cells. Nevertheless, every cloud has a silver lining. The immunosuppressive components also shed new inspiration on reshaping a friendly TIME by targeting them with engineered CARs. Herein, we summarize recent advances in disincentives of TIME and discuss approaches and technologies to enhance CAR-T cell efficacy via addressing current hindrances. Simultaneously, we firmly believe that by parsing the immunosuppressive components of TIME, rationally manipulating the complex interactions of immunosuppressive components, and optimizing CAR-T cell therapy for each patient, the CAR-T cell immunotherapy responsiveness for solid malignancies will be substantially enhanced, and novel therapeutic targets will be revealed.
Keywords: Tumor immune microenvironment, immunotherapy, chimeric antigen receptor T cell, immunosuppression network, solid tumors
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact