13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(13):5631-5644. doi:10.7150/thno.60636 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Lgr5+ cells are required and dynamically participate in olfactory epithelium regeneration: a revisiting shows Lgr5 expression in multiple cell lineages
1. Ear, Nose & Throat Institute, Department of Otolaryngology, Eye, Ear, Nose & Throat Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200031, China.
2. Department of Otolaryngology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of the Naval Military Medical University (Shanghai Changzheng Hospital), Shanghai, China.
3. School of Life Sciences, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China.
4. Clinical and Research Center for Olfactory Disorders, Eye, Ear, Nose & Throat Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200031, China.
5. Research Units of New Technologies of Endoscopic Surgery in Skull Base Tumor, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China.
Abstract
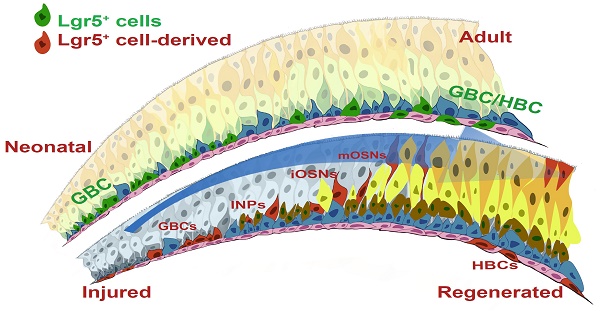
Olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) located in the olfactory epithelium (OE) detect thousands of volatile environmental odors to form the sense of smell. OSNs are generated from basal cells, which show the characteristics of progenitor/stem cells. In the mammalian OE, persistent neurogenesis occurs during lifetime, providing a unique model to study the tissue turnover and fate determination of stem cells.
Methods: Immunohistochemical analysis and RNAscope in situ hybridization indicated the localization of leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 (Lgr5) in the intact and injured OE. Lineage tracing was conducted to analyze the dynamic role of Lgr5+ cells in the OE homeostasis and regeneration. We also used DTR-driven genetic depletion of Lgr5+ cells and lentivirus-mediated Lgr5 downregulation to demonstrate the essential role of Lgr5+ cells in the OE regeneration.
Results: We show that Lgr5 marks horizontal basal cells (HBCs) in the OE of adults but not newborns. We revisit the role of Lgr5+ cells in the OE homeostasis and regeneration, and find that Lgr5+ cells participate in the OE homeostasis from neonatal to one-month-old age, as well as in the OE regeneration post injury. During the OE regeneration, Lgr5 is transiently expressed in apical supporting cells, immature neurons, and mature sensory neurons. The Lgr5+ cells become or generate HBCs in the regenerated OE. DTR-driven cell depletion shows that Lgr5+ cells are not necessary in the adult OE homeostasis, but required in the recovery of OE from injury. Lgr5 down-regulation by lentiviral infection also demonstrates the essential role of Lgr5 expression in the OE regeneration.
Conclusion: Our study elucidates the role of Lgr5+ cells in the OE homeostasis and regeneration, potentially providing a candidate to cell-based therapy against olfactory dysfunction.
Keywords: Lgr5, olfactory epithelium, regeneration, olfactory sensory neuron, globose basal cell, horizontal basal cell
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact