13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(11):4965-4979. doi:10.7150/thno.73152 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Docetaxel remodels prostate cancer immune microenvironment and enhances checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy
1. Department of Urology, Ren Ji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China.
2. Shanghai Key Laboratory for Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammation, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
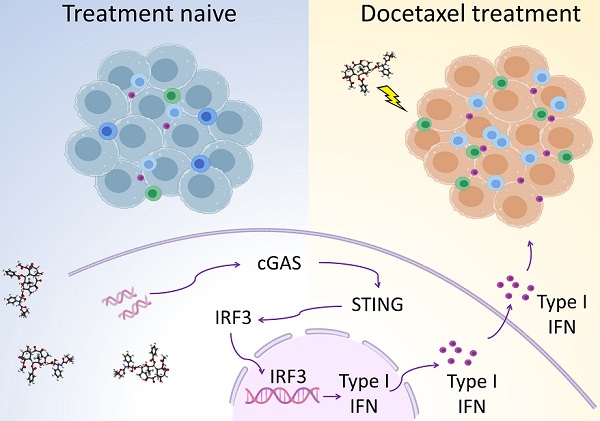
Background: Prostate cancer is usually considered as immune “cold” tumor with poor immunogenic response and low density of tumor-infiltrating immune cells, highlighting the need to explore clinically actionable strategies to sensitize prostate cancer to immunotherapy. In this study, we investigated whether docetaxel-based chemohormonal therapy induces immunologic changes and potentiates checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in prostate cancer.
Methods: We performed transcriptome and histopathology analysis to characterize the changes of prostate cancer immune microenvironment before and after docetaxel-based chemohormonal therapy. Furthermore, we investigated the therapeutic benefits and underlying mechanisms of chemohormonal therapy combined with anti-PD1 blockade using cellular experiments and xenograft prostate cancer models. Finally, we performed a retrospective cohort analysis to evaluate the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD1 blockade alone or in combination with docetaxel-based chemotherapy.
Results: Histopathology assessments on patient samples confirmed the enrichment of tumor-infiltrating T cells after chemohormonal therapy. Moreover, we found that docetaxel activated the cGAS/STING pathway in prostate cancer, subsequently induced IFN signaling, resulting in lymphocytes infiltration. In a xenograft mouse model, docetaxel-based chemohormonal therapy prompted the intratumoral infiltration of T cells and upregulated the abundance of PD1 and PD-L1, thereby sensitizing mouse tumors to the anti-PD1 blockade. To determine the clinical significance of these results, we retrospectively analyzed a cohort of 30 metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients and found that docetaxel combined with anti-PD1 blockade resulted in better prostate-specific antigen progression-free survival when compared with anti-PD1 blockade alone.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates that docetaxel activates the antitumoral immune response and facilitates T cell infiltration in a cGAS/STING-dependent manner, providing a combination immunotherapy strategy that would improve the clinical benefits of immunotherapy.
Keywords: Prostate Cancer, Docetaxel, cGAS/STING, Immunotherapy, Immune microenvironment
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact