13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(3):1373-1387. doi:10.7150/thno.63359 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Three-dimensional colon cancer organoids model the response to CEA-CD3 T-cell engagers
1. Program of Immunology and Immunotherapy. Cima Universidad de Navarra. 31008. Pamplona, Spain.
2. Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Cáncer (CIBERONC), Madrid, Spain.
3. Navarra Institute for Health Research (IDISNA), 31008, Pamplona, Spain.
4. Departments of Oncology and Immunology. Clinica Universidad de Navarra, 31008, Pamplona, Spain.
5. Roche Pharmaceutical Research & Early Development, Roche Innovation Center Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland.
*These authors share senior authorship.
Abstract
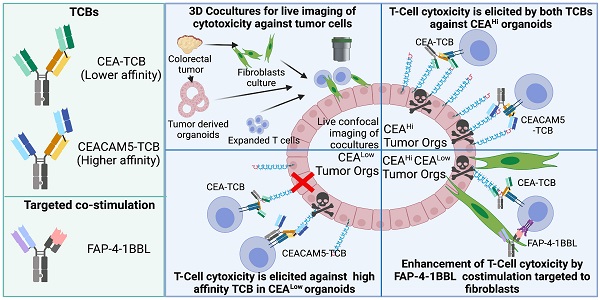
Rationale: The CEA-CD3 T cell bispecific antibody cibisatamab (CEA-TCB) is currently undergoing clinical trials. Here we study its performance against three-dimensional tumor organoids in cocultures with T cells as compared to a higher affinity CEACAM5-CD3 (CEACAM5-TCB) bispecific antibody using time-lapse confocal microscopy.
Methods: Pre-labelled spheroids derived from colon cancer cell lines and primary organoids derived from four colorectal cancer surgical specimens, which expressed different graded levels of CEA, were exposed in cocultures to T lymphocytes. Cocultures were treated with CEA-CD3 T-cell engagers and were followed by live confocal microscopy. Caspase 3 activation detected in real-time was used as an indicator of tumor cell death. Co-cultures were also set up with autologous tumor-associated fibroblasts to test the co-stimulatory effect of a fibroblast activated protein (FAP)- targeted 4-1BBL bispecific antibody fusion protein currently undergoing clinical trials.
Results: Tumor-cell killing of 3D colon carcinoma cultures was dependent on the levels of surface CEA expression, in such a way that the lower affinity agent (CEA-TCB) did not mediate killing by human preactivated T cells below a certain CEA expression threshold, while the high affinity construct (CEACAM5-TCB) remained active on the low CEA expressing organoids. Modelling heterogeneity in the levels of CEA expression by coculturing CEA high and low organoids showed measurable but weak bystander killing. Cocultures of tumor organoids, autologous fibroblasts and T cells allowed to observe a costimulatory effect of anti-FAP-4-1BBL both to release IFNγ and to attain more efficacious tumor cell killing.
Conclusion: Three-dimensional tumor cocultures with T cells using live confocal microscopy provide suitable models to test the requirements for colon-cancer redirected killing as elicited by CEA-targeted T-cell engagers undergoing clinical trials and treatment allow combinations to be tested in a relevant preclinical system.
Keywords: Colon organoids, T-cell engager, colon cancer, live confocal microscopy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact