13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(3):1161-1172. doi:10.7150/thno.67515 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Type 2 innate immunity drives distinct neonatal immune profile conducive for heart regeneration
1. School of Life Sciences, Faculty of Science, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
3. Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
4. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Ionic-Molecular Function of Cardiovascular Disease, Department of Cardiology, Tianjin Institute of Cardiology, Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China.
5. Kent and Medway Medical School, Canterbury, United Kingdom.
6. Department of Medicine, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
7. Merck Research Labs, SAF-803, South San Francisco, CA, USA.
8. School of Biomedical Sciences, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
9. State Key Laboratory of Agrobiotechnology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
Abstract
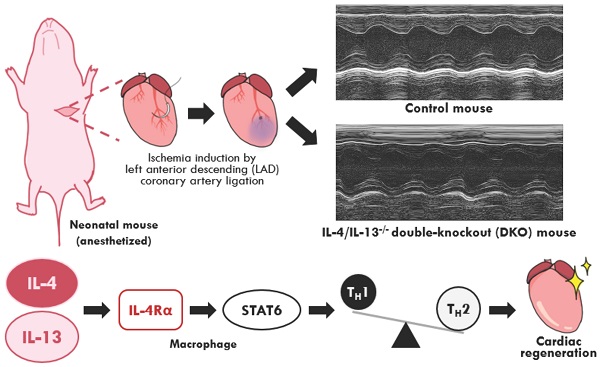
Aims: Neonatal immunity is functionally immature and skewed towards a TH2-driven, anti-inflammatory profile. This neonatal immunotolerance is partly driven by the type 2 cytokines: interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13). Studies on neonatal cardiac regeneration reveal the beneficial role of an anti-inflammatory response in restoring cardiac function after injury. However, the role of an imbalanced immune repertoire observed in neonates on tissue regeneration is poorly understood; specifically, whether IL-4 and IL-13 actively modulate neonatal immunity during cardiac injury.
Methods and results: Neonatal mice lacking IL-4 and IL-13 (DKOs) examined at 2 days after birth exhibited reduced anti-inflammatory immune populations with basal cardiac immune populations like adult mice. Examination of neonates lacking IL-4 and IL-13 at 2 days post cardiac ischemic injury, induced on the second day after birth, showed impaired cardiac function compared to their control counterparts. Treatment with either IL-4 or IL-13 cytokine during injury restored both cardiac function and immune population profiles in knockout mice. Examination of IL-4/IL-13 downstream pathways revealed the role of STAT6 in mediating the regenerative response in neonatal hearts. As IL-4/IL-13 drives polarization of alternatively activated macrophages, we also examined the role of IL-4/IL-13 signaling within the myeloid compartment during neonatal cardiac regeneration. Injury of IL-4Rα myeloid specific knockout neonates 2 days after birth revealed that loss of IL-4/IL-13 signaling in macrophages alone was sufficient to impair cardiac regeneration.
Conclusions: Our results confirm that the TH2 cytokines: IL-4 and IL-13, which skews neonatal immunity to a TH2 profile, are necessary for maintaining and mediating an anti-inflammatory response in the neonatal heart, in part through the activation of alternatively activated macrophages, thereby permitting a niche conducive for regeneration.
Keywords: IL-4, IL-13, neonatal heart regeneration, TH2 immunity, alternatively activated macrophages, left anterior descending coronary artery ligation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact