13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(1):410-417. doi:10.7150/thno.67155 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Simultaneous enhancement of T1 and T2 magnetic resonance imaging of liver tumor at respective low and high magnetic fields
1. Department of Radiology, the Second Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui 230601, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Structure and Functional Regulation of Hybrid Materials, Ministry of Education, Institutes of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, Anhui 230601, China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Bioelectronics, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210096, China.
4. High Magnetic Field Laboratory, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui 230031, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
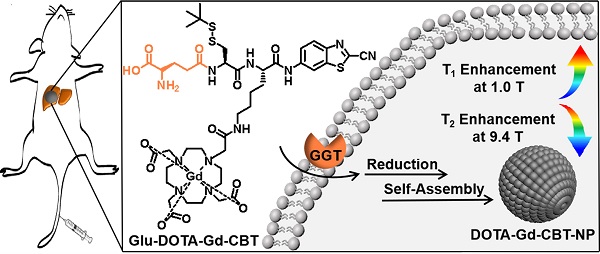
Background: Nowadays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is routinely applied in clinical diagnosis. However, using one contrast agent (CA) to simultaneously enhance the T1 and T2 MR contrast at low and high magnetic fields respectively has not been reported.
Methods: Herein, we investigated the MR property of a γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)-instructed, intracellular formed gadolinium nanoparticle (DOTA-Gd-CBT-NP) at low and high magnetic fields.
Results: Experimental results showed that DOTA-Gd-CBT-NP possesses a low r2/r1 ratio 0.91 which enables it to enhance T1 MR imaging of liver tumor at 1.0 T, and a high r2/r1 ratio 11.8 which renders the nanoparticle to largely enhance T2 MR imaging of liver tumor at 9.4 T.
Conclusion: We expect that our GGT-responsive Gd-nanoparticle could be applied for simultaneous T1 and T2 MRI diagnosis of early liver cancer in clinic at respective low and high magnetic fields when the 9.4 T MR machine is clinically available in the future.
Keywords: γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, gadolinium nanoparticle, magnetic resonance imaging, liver tumor, tumor imaging
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact