13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(1):324-339. doi:10.7150/thno.63735 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tubular epithelial cell-to-macrophage communication forms a negative feedback loop via extracellular vesicle transfer to promote renal inflammation and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
1. Inflammation and Immune Mediated Diseases Laboratory of Anhui Province, Anhui Institute of Innovative Drugs, School of Pharmacy, Anhui Medical University, Hefei, 230032, China.
2. The Center for Scientific Research of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, 230032, China.
* These authors contributed equally to the first author.
Abstract
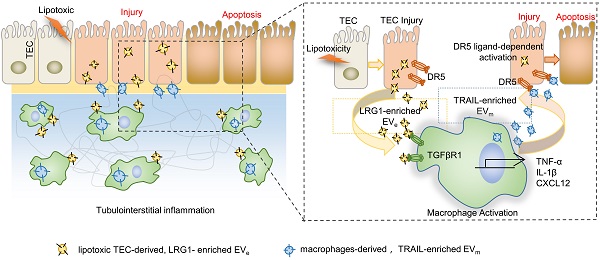
Background: Macrophage infiltration around lipotoxic tubular epithelial cells (TECs) is a hallmark of diabetic nephropathy (DN). However, how these two types of cells communicate remains obscure. We previously demonstrated that LRG1 was elevated in the process of kidney injury. Here, we demonstrated that macrophage-derived, LRG1-enriched extracellular vesicles (EVs) exacerbated DN.
Methods: We induced an experimental T2DM mouse model with a HFD diet for four months. Renal primary epithelial cells and macrophage-derived EVs were isolated from T2D mice by differential ultracentrifugation. To investigate whether lipotoxic TEC-derived EV (EVe) activate macrophages, mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were incubated with EVe. To investigate whether activated macrophage-derived EVs (EVm) induce lipotoxic TEC apoptosis, EVm were cocultured with primary renal tubular epithelial cells. Subsequently, we evaluated the effect of LRG1 in EVe by investigating the apoptosis mechanism.
Results: We demonstrated that incubation of primary TECs of DN or HK-2 mTECs with lysophosphatidyl choline (LPC) increased the release of EVe. Interestingly, TEC-derived EVe activated an inflammatory phenotype in macrophages and induced the release of macrophage-derived EVm. Furthermore, EVm could induce apoptosis in TECs injured by LPC. Importantly, we found that leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein 1 (LRG1)-enriched EVe activated macrophages via a TGFβR1-dependent process and that tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-enriched EVm induced apoptosis in injured TECs via a death receptor 5 (DR5)-dependent process.
Conclusion: Our findings indicated a novel cell communication mechanism between tubular epithelial cells and macrophages in DN, which could be a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy, extracellular vesicles, leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein 1, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, death receptor 5, tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact