13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(1):48-58. doi:10.7150/thno.65302 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Mucosal microbiome associates with progression to gastric cancer
1. Department of Microbiology & Immunology, and NUSMED Immunology Translational Research Programme, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117456, Singapore.
2. Immunology Programme, Life Science Institute, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117456, Singapore.
3. Department of Medicine, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore 119228, Singapore.
4. Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, National University Health System, Singapore 119074, Singapore.
5. Singapore Gastric Cancer Consortium, Singapore 119074, Singapore.
*Co-first authors
Abstract
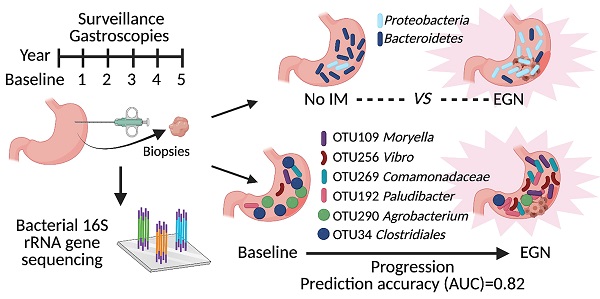
Background & Aims: Dysbiosis is associated with gastric cancer (GC) development. However, no longitudinal study was carried out to identify key bacteria that could predict for GC progression. Here, we aimed to investigate changes in bacterial metagenome prior to GC and develop a microbiome-based predictive model to accurately classify patients at risk of GC.
Methods: Bacterial 16S rDNA was sequenced from 89 gastric antral biopsies obtained from 43 participants. This study was nested in a prospective, longitudinal study, whereby study participants underwent screening gastroscopy, with further 1-2 yearly surveillance gastroscopies for at least 5 years. Putative bacterial taxonomic and functional features associated with GC carcinogenesis were identified by comparing between controls, patients with gastric intestinal metaplasia (IM) and patients with early gastric neoplasia (EGN).
Results: Patients with EGN had enrichment of Proteobacteria (in particular Proteus genus) and depletion of Bacteroidetes (in particular S24-7 family) in their gastric mucosa. Sequencing identified more patients with Helicobacter pylori compared to histopathological assessment, while H. pylori was also significantly enriched in EGN. Furthermore, a total of 261 functional features, attributing to 97 KEGG pathways were differentially abundant at baseline between patients who subsequent developed EGN (n = 13/39) and those who did not. At the same time, a constellation of six microbial taxonomic features present at baseline, provided the highest classifying power for subsequent EGN (AUC = 0.82).
Conclusion: Our study highlights early microbial changes associated with GC carcinogenesis, suggesting a potential role for prospective microbiome surveillance for GC.
Keywords: gastric cancer, microbiome, intestinal metaplasia, early gastric neoplasia, Helicobacter pylori
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact