13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(9):4103-4121. doi:10.7150/thno.53418 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MicroRNA-146a switches microglial phenotypes to resist the pathological processes and cognitive degradation of Alzheimer's disease
1. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Age-Related Cardiac and Cerebral Diseases, Institute of Neurology, Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang, China.
2. Department of Neurology, Yuebei People's Hospital Affiliated to Shantou University, Shaoguan, China.
3. Department of Pharmacology and Neuroscience, University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, TX, USA.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
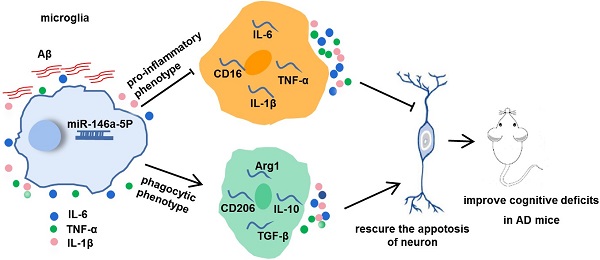
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease and currently has no effective treatment. Mainstream research on the mechanisms and therapeutic targets of AD is focused on the two most important hallmarks, Aβ and Tau, but the results from clinical studies are not encouraging. Abnormal microglial polarization is a clear typical pathological feature in the progression of AD. Microglia can be neuroprotective by degrading and removing Aβ and Tau. However, under AD conditions, microglia transform into a pro-inflammatory phenotype that decreases the phagocytic activity of microglia, damages neurons and promotes the pathology of AD. We previously reported that a miR-146a polymorphism is associated with sporadic AD risk, and the nasal administration of miR-146a mimics reduced cognitive impairment and the main pathological features of AD. However, it is not clear by what mechanism miR-146a resists the pathological process of AD. In this study, we discovered that microglia-specific miR-146a overexpression reduced cognitive deficits in learning and memory, attenuated neuroinflammation, reduced Aβ levels, ameliorated plaque-associated neuritic pathology, and prevented neuronal loss in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. In addition, we found that miR-146a switched the microglial phenotype, reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhanced phagocytic function to protect neurons in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, transcriptional analysis confirmed that miR-146a opposed the pathological process of AD mainly through neuroinflammation-related pathways. In summary, our results provide sufficient evidence for the mechanism by which miR-146a opposes AD and strengthen the conclusion that miR-146a is a promising target for AD and other microglia-related diseases.
Keywords: microRNA-146a, Alzheimer's disease, microglial polarization, neuroinfammation, phagocytic activity.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact