13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(7):3376-3391. doi:10.7150/thno.52190 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hypoxia-induced Nur77 activates PI3K/Akt signaling via suppression of Dicer/let-7i-5p to induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
1. School of Biological Sciences, University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong.
2. State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology and Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Innovative Drug Target Research, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China.
#These authors made equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
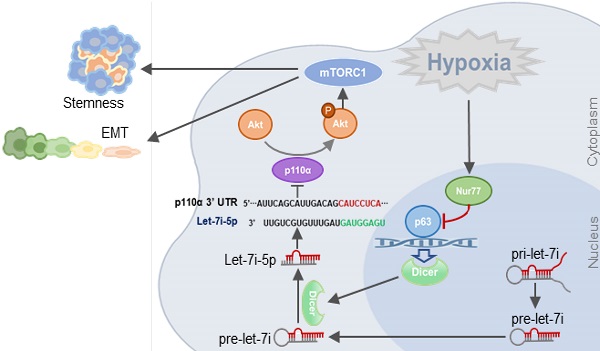
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) and the associated metastatic lesions are reported to be hypoxic. Hypoxia is a common feature in the tumor microenvironment and a potent stimulant of CRC. We have identified a regulatory role of Nur77 on Akt activation to enhance β-catenin signaling essential for CRC progression under hypoxic conditions.
Methods: The functional role of Nur77 in hypoxia-induced EMT was examined by scattering assays to monitor the morphologies of CRC cell lines under 1% O2. Sphere formation assays were performed to investigate whether Nur77 induced cancer stem cell-like properties in hypoxic CRC cells. The expression of various epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and stemness markers was analyzed by qPCR and Western blotting. Finally, Nur77 function and signaling in vivo was ascertained in subcutaneous tumor xenograft or liver metastasis model in nude mice using CRC cells stably transfected with appropriate constructs.
Results: Herein, we show, for the first time, that Nur77 is a novel regulator of microRNA biogenesis that may underlie its significant tumor-promoting activities in CRC cells under hypoxia. Mechanistically, Nur77 interacted with the tumor suppressor protein p63, leading to the inhibition of p63-dependent transcription of Dicer, an important miRNA processor and subsequent decrease in the biogenesis of let-7i-5p which targeted the 3'UTR of p110α mRNA and regulated its stability. Knockdown of Nur77 or overexpression of let-7i-5p inhibited the tumor metastasis in vivo.
Conclusion: Our data uncovered a novel mechanistic link connecting Nur77, Akt, and invasive properties of CRC in the hypoxic microenvironment.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, hypoxia, Nur77, microRNA biogenesis, PI3K/Akt, EMT
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact