13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(7):3131-3149. doi:10.7150/thno.52677 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Conditioned medium from adipose-derived stem cells attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury through the microRNA-221/222/PUMA/ETS-1 pathway
1. Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
2. Department of Bioscience Technology, College of Science, Chung-Yuan Christian University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
3. Center for Nanotechnology and Center for Biomedical Technology, Chung-Yuan Christian University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
4. Department of Clinical Laboratory Sciences and Medical Biotechnology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
5. Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
6. Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Cathay General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
7. School of Dentistry, College of Oral Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
8. Department of Family Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
9. Center for Complementary and Integrated Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
10. Department of Nursing, Division of Basic Medical Sciences, and Chronic Diseases and Health Promotion Research Center, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Chiayi, Taiwan.
11. Research Center for Industry of Human Ecology and Research Center for Chinese Herbal Medicine, Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
12. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Taiwan.
Abstract
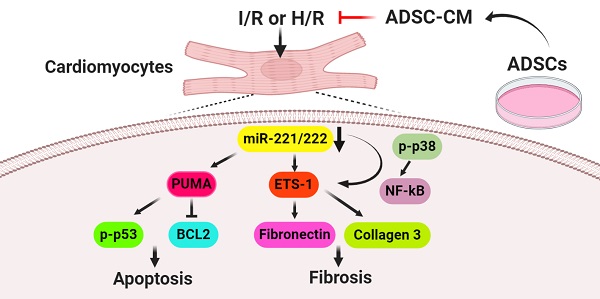
Rationale: Cardiovascular diseases, such as myocardial infarction (MI), are the leading causes of death worldwide. Reperfusion therapy is the common standard treatment for MI. However, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) causes cardiomyocyte injury, including apoptosis and fibrosis. We aimed to investigate the effects of conditioned medium from adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC-CM) on apoptosis and fibrosis in I/R-treated hearts and hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-treated cardiomyocytes and the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: ADSC-CM was collected from ADSCs. The effects of intramuscular injection of ADSC-CM on cardiac function, cardiac apoptosis, and fibrosis examined by echocardiography, Evans blue/TTC staining, TUNEL assay, and Masson's trichrome staining in I/R-treated mice. We also examined the effects of ADSC-CM on apoptosis and fibrosis in H/R-treated H9c2 cells by annexin V/PI flow cytometry, TUNEL assay, and immunocytochemistry.
Results: ADSC-CM treatment significantly reduced heart damage and fibrosis of I/R-treated mice and H/R-treated cardiomyocytes. In addition, the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, such as p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA), p-p53 and B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2), as well as the fibrosis-related proteins ETS-1, fibronectin and collagen 3, were significantly reduced by ADSC-CM treatment. Moreover, we demonstrated that ADSC-CM contains a large amount of miR-221/222, which can target and regulate PUMA or ETS-1 protein levels. Furthermore, the knockdown of PUMA and ETS-1 decreased the induction of apoptosis and fibrosis, respectively. MiR-221/222 overexpression achieved similar results. We also observed that cardiac I/R markedly increased apoptosis and fibrosis in miR-221/222 knockout (KO) mice, while ADSC-CM decreased these effects. The increased phosphorylation of p38 and NF‐κB not only mediated myocardial apoptosis through the PUMA/p53/BCL2 pathway but also regulated fibrosis through the ETS-1/fibronectin/collagen 3 pathway.
Conclusions: Overall, our results show that ADSC-CM attenuates cardiac apoptosis and fibrosis by reducing PUMA and ETS-1 expression, respectively. The protective effect is mediated via the miR-221/222/p38/NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: Ischemia/reperfusion injury, ADSC-CM, miR-221/222, apoptosis, fibrosis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact