13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(20):10012-10029. doi:10.7150/thno.66478 This issue Cite
Review
Microneedle arrays integrated with living organisms for smart biomedical applications
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
2. Department of Pharmacology, School of Basic Medicine, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China.
3. Hubei Key Laboratory for Drug Target Research and Pharmacodynamic Evaluation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China.
4. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
5. Research Center for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
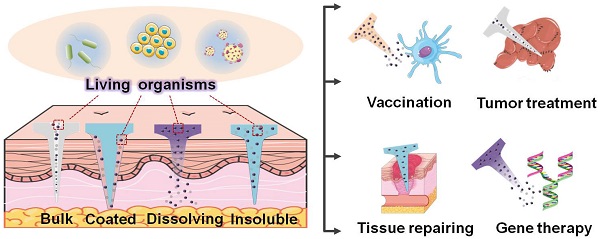
Various living organisms have proven to influence human health significantly, either in a commensal or pathogenic manner. Harnessing the creatures may remarkably improve human healthcare and cure the intractable illness that is challenged using traditional drugs or surgical approaches. However, issues including limited biocompatibility, poor biosafety, inconvenience for personal handling, and low patient compliance greatly hinder the biomedical and clinical applications of living organisms when adopting them for disease treatment. Microneedle arrays (MNAs), emerging as a promising candidate of biomedical devices with the functional diversity and minimal invasion, have exhibited great potential in the treatment of a broad spectrum of diseases, which is expected to improve organism-based therapies. In this review, we systemically summarize the technologies employed for the integration of MNAs with specific living organisms including diverse viruses, bacteria, mammal cells and so on. Moreover, their applications such as vaccination, anti-infection, tumor therapy and tissue repairing are well illustrated. Challenges faced by current strategies, and the perspectives of integrating more living organisms, adopting smarter materials, and developing more advanced technologies in MNAs for future personalized and point-of-care medicine, are also discussed. It is believed that the combination of living organisms with functional MNAs would hold great promise in the near future due to the advantages of both biological and artificial species.
Keywords: microneedle, living organism, smart integration, vaccination, anti-infection, cell-based therapy, cell and secretion delivery
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact