13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(21):9528-9543. doi:10.7150/thno.42971 This issue Cite
Research Paper
m6A RNA modification modulates PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal pathway in Gastrointestinal Cancer
1. Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, 646000, Sichuan, PR China.
2. South Sichuan Institute of Translational Medicine, Luzhou, 646000, Sichuan, PR China.
3. Department of Pathophysiology, College of Basic Medical Science, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, 646000, Sichuan, PR China.
4. Department of Gastroenterology, Shenzhen Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, PR China.
5. Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, PR China.
6. Department of Oncology, Jiangsu Cancer Hospital and Jiangsu Institute of Cancer Research and The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210000, PR China.
7. Clinical Medical Research Center, the Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Southern University, Shenzhen People's Hospital, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518020, PR China.
8. Department of Breast and Thyroid Surgery, the Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, The First Affiliated Hospital of Southern University, Shenzhen People's Hospital, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518020, PR China.
9. Department of Pharmacy, Yijishan Affiliated Hospital of Wannan Medical College, Wuhu, Anhui, PR China.
10. Department of Hematology and Oncology, The Children's Hospital of Soochow, Jiangsu, PR China.
11. Department of Oncology, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan 646000, PR China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
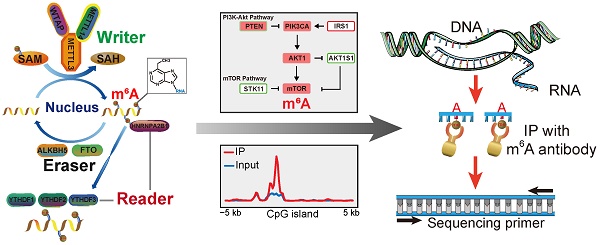
Rationale: Methylation at the N6 position of adenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent RNA modification within protein-coding mRNAs in mammals, and it is a reversible modification with various important biological functions. The formation and function of m6A are regulated by methyltransferases (writers), demethylases (erasers), and special binding proteins (readers) as key factors. However, the underlying modification mechanisms of m6A in gastrointestinal (GI) cancer remain unclear. Here, we performed comprehensive molecular profiling of the nine known m6A writer, eraser, and reader proteins in GI cancer.
Methods: Data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) were used. Gene alteration and pathway analysis were done in cBioportal. The protein network of m6A regulators and its related pathway members was analyzed in STRING online platform. Phylogenetic tree was constructed in MEGA7. m6A modification sites were predicted by SRAMP. m6A related SNPs were analyzed by m6ASNP. The modulation of m6A on its related pathway members was validated by m6A-seq, real-time PCR and phosphor-MAPK array.
Results: We found that m6A regulators were mostly upregulated in GI cancer and their differential expression significantly influenced the overall survival of patients with GI cancer. The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways were found to be potentially affected by m6A modification in most human cancers, including GI cancer, which was further verified by m6A-Seq and phospho-MAPK array.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that m6A RNA modification has a fundamental role in the regulation of PI3K/Akt and mTOR signaling pathway function in cancer.
Keywords: m6A RNA methylation, gastrointestinal cancer, bioinformatics, PI3K/Akt signal pathway, mTOR signaling pathway
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact