13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(14):6399-6410. doi:10.7150/thno.45816 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Autoantibody profiling identifies predictive biomarkers of response to anti-PD1 therapy in cancer patients
1. Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing Key Laboratory of Clinical Study on Anticancer Molecular Targeted Drugs, Beijing 100021, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Proteomics, Beijing Proteome Research Center, National Center for Protein Sciences-Beijing (PHOENIX Center), Beijing Institute of Lifeomics, Beijing 102206, China.
3. Clinical Pharmacology Research Center, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing Key Laboratory of Clinical PK & PD Investigation for Innovative Drugs, Beijing 100032, China.
* Contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
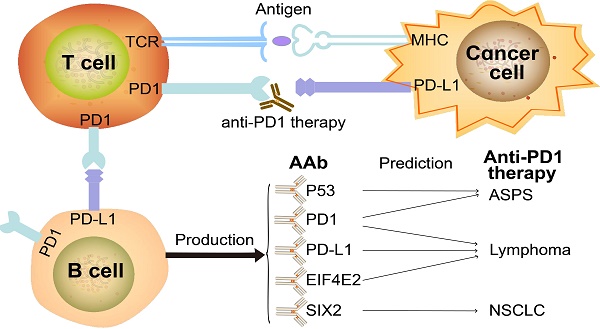
Background: Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1) inhibitors have revolutionized cancer therapy, yet many patients fail to respond. Thus, the identification of accurate predictive biomarkers of therapy response will improve the clinical benefit of anti-PD1 therapy.
Method: We assessed the baseline serological autoantibody (AAb) profile against ~2300 proteins in 10 samples and ~4600 proteins in 35 samples with alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS), non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and lymphoma using Nucleic Acid Programmable Protein Arrays (NAPPA). 23 selected potential AAb biomarkers were verified using simple, affordable and rapid enzyme linked immune sorbent assay (ELISA) technology with baseline plasma samples from 12 ASPS, 16 NSCLC and 46 lymphoma patients. SIX2 and EIF4E2 AAbs were further validated in independent cohorts of 17 NSCLC and 43 lymphoma patients, respectively, using ELISA. The IgG subtypes in response to therapy were also investigated.
Results: Distinct AAb profiles between ASPS, NSCLC and lymphoma were observed. In ASPS, the production of P53 and PD1 AAbs were significantly increased in non-responders (p=0.037). In NSCLC, the SIX2 AAb was predictive of response with area under the curve (AUC) of 0.87, 0.85 and 0.90 at 3 months, 4.5 months, 6 months evaluation time points, respectively. In the validation cohort, the SIX2 AAb was consistently up-regulated in non-responders (p=0.024). For lymphoma, the EIF4E2 AAb correlated with a favorable response with AUCs of 0.68, 0.70, and 0.70 at 3 months, 4.5 months, and 6 months, respectively. In the validation cohort, the AUCs were 0.74, 0.75 and 0.66 at 3 months, 4.5 months, and 6 months, respectively. The PD1 and PD-L1 IgG2 AAbs were highly produced in ~20% of lymphoma responders. Furthermore, bioinformatics analysis revealed antigen functions of these AAb biomarkers.
Conclusion: This study provides the first evidence that AAb biomarkers selected using high-throughput protein microarrays can predict anti-PD1 therapeutic response and guide anti-PD1 therapy.
Keywords: Anti-PD1 therapy, Autoantibody, Biomarker, Protein microarray
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact