13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(13):5998-6010. doi:10.7150/thno.43427 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Investigation of the role and mechanism of ARHGAP5-mediated colorectal cancer metastasis
1. Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou 510060, China
2. The Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510630, China
*These authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
Background: Metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) is a lethal disease; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear and require further study.
Methods: RNA-Seq, PCR, Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, ChIP and RNAi assays were performed to investigate Rho GTPase-activating protein 5 (ARHGAP5, aslo known as p190RhoGAP-B, p190-B) expression and the clinical relevance, functional roles and regulatory mechanisms of this protein using human CRC cells and tissues. In vivo, two cell-based xenograft models were used to evaluate the roles of ARHGAP5 in CRC metastasis.
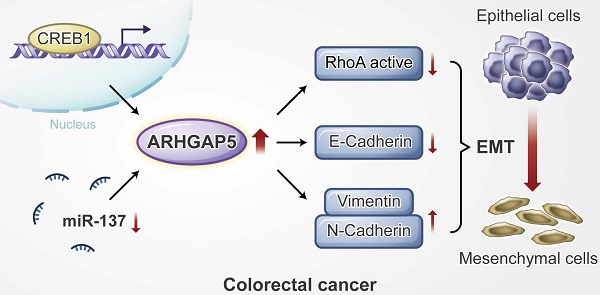
Results: Here, we report that ARHGAP5 expression is significantly increased in metastatic CRC tissues and is inversely associated with patient overall survival. The suppression of ARHGAP5 reduces CRC cell metastasis in vitro and in cell-based xenograft models. Furthermore, we show that ARHGAP5 promotes CRC cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition by negatively regulating RhoA activity. Mechanistically, cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB1) transcriptionally upregulates ARHGAP5 expression, and decreased miR-137 further contributes to ARHGAP5 mRNA stability in CRC.
Conclusions: Overall, our study highlights the crucial function of ARHGAP5 in CRC metastasis, thus suggesting novel prognostic biomarkers and hypothetical therapeutic targets.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, tumor metastasis, ARHGAP5, CREB1, miR-137
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact