13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(11):4795-4808. doi:10.7150/thno.42922 This issue Cite
Research Paper
pH responsive superporogen combined with PDT based on poly Ce6 ionic liquid grafted on SiO2 for combating MRSA biofilm infection
1. Department of pharmacy, Air Force Medical University, Xi'an, 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
2. Department of physics, Northwest University of Technology, Xi'an, 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
3. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Tangdu Hospital, Air Force Medical University, Xi'an, 710032, Shaanxi Province, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
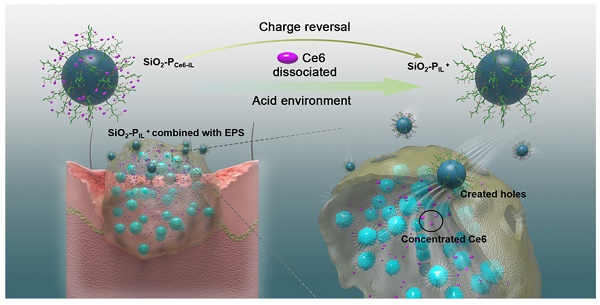
Background: Biofilm infection caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria is difficult to eradicate by conventional therapies. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an effective antibacterial method for fighting against biofilm infection. However, the blocked photosensitizers outside of biofilm greatly limit the efficacy of PDT.
Methods: Herein, a novel acid-responsive superporogen and photosensitizer (SiO2-PCe6-IL) was developed. Because of the protonation of the photosensitizer and the high binding energy of the polyionic liquid, SiO2-PCe6-IL changed to positive SiO2-PIL+ in an acidic microenvironment of biofilm infection. SiO2-PIL+ could combine with negatively charged extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and create holes to remove the biofilm barrier. To strengthen the interaction between SiO2-PIL+ and EPS, SiO2-PIL+ of high charge density was prepared by grafting the high-density initiation site of ATRP onto the surface of the SiO2 base.
Results: Due to the rapid protonation rate of COO- and the strong binding energy of SiO2-PIL+ with EPS, SiO2-PCe6-IL could release 90% of Ce6 in 10 s. With the stronger electrostatic and hydrophobic interaction of SiO2-PIL+ with EPS, the surface potential, hydrophobicity, adhesion and mechanical strength of biofilm were changed, and holes in the biofilm were created in 10 min. Combining with the release of photosensitizers and the porous structure of the biofilm, Ce6 was efficiently concentrated in the biofilm. The in vitro and in vivo antibacterial experiments proved that SiO2-PCe6-IL dramatically improved the PDT efficacy against MRSA biofilm infection.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that SiO2-PCe6-IL could rapidly increase the concentration of photosensitizer in biofilm and it is an effective therapy for combating biofilm infection.
Keywords: pH-responsive, polyionic liquids, superporogen, photosensitizer, SiO2, MRSA biofilm
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact