13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(23):10563-10572. doi:10.7150/thno.48522 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Association of sex and APOE ε4 with brain tau deposition and atrophy in older adults with Alzheimer's disease
1. Department of Radiology, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
2. Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA.
3. Harvard-MIT Program in Health Sciences and Technology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
4. Department of Neurology, Washington in St. Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA.
Abstract
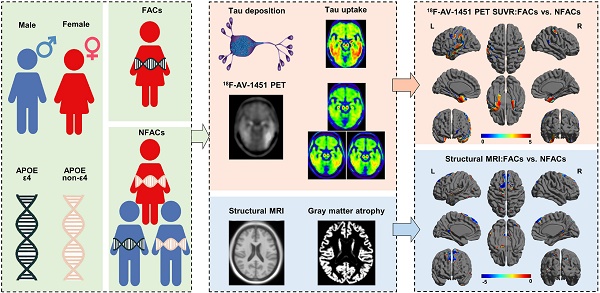
The objective of this study was to assess the association of sex and the apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 allele with brain tau deposition and atrophy in older adults with Alzheimer's disease (AD) using quantitative 18F-AV-1451 positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods: Preprocessed 18F-AV-1451 tau PET, raw T1-weighted structural MR images, demographic information, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) total tau (t-tau) and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) measurements from 57 elderly individuals with AD were downloaded from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database. An iteratively reblurred Van Cittert partial volume correction (PVC) method was applied to all preprocessed PET images. MRI images were used for PET spatial normalization and gray matter volume calculation. 18F-AV-1451 PET standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR) was calculated relative to the cerebellum gray matter. The effect of sex and APOE ε4 status on SUVR and gray matter volume were assessed at both region of interest (ROI) and voxelwise levels.
Results: Female APOE ε4 carriers (FACs) had significant higher 18F-AV-1451 SUVRs in the lateral temporal, parietal, posterior cingulate, medial temporal, inferior temporal, entorhinal cortex, amygdala and parahippocampal gyrus regions, and exhibited smaller gray matter volumes in the posterior cingulate, medial temporal, inferior temporal and amygdala regions, as compared to the non-FACs (NFACs) comprised of female APOE ε4 non-carriers, male APOE ε4 carriers and male APOE ε4 non-carriers. Voxelwise analysis revealed forebrain and limbic clusters with greater 18F-AV-1451 SUVRs and lower gray matter volume between FACs compared to the NFACs. Negative correlations between ROI 18F-AV-1451 SUVRs and gray matter volumes were significant after adjusting for age and years of education.
Conclusions: Among elderly individuals with AD, sex modified the effects of the APOE ε4 allele on region-specific tau deposition and gray matter volume. FACs had elevated brain region-specific tau PET SUVR and decreased gray matter volume in comparison to NFACs. The study provides a basis for the use of precision medicine in the diagnosis of AD and evaluation of therapeutics using 18F-AV-1451 PET and structural MRI.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease, Tau PET, Sex, APOE, Neurodegeneration
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact