13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(23):10360-10377. doi:10.7150/thno.49922 This issue Cite
Review
Managing therapeutic resistance in breast cancer: from the lncRNAs perspective
1. State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital, and West China School of Basic Medical Sciences & Forensic Medicine, Sichuan University, and Collaborative Innovation Center for Biotherapy, Chengdu, 610041, P.R. China.
2. Department of Urology, Institute of Urology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, P.R. China.
3. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia.
4. West China School of Basic Medical Sciences & Forensic Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, P.R. China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
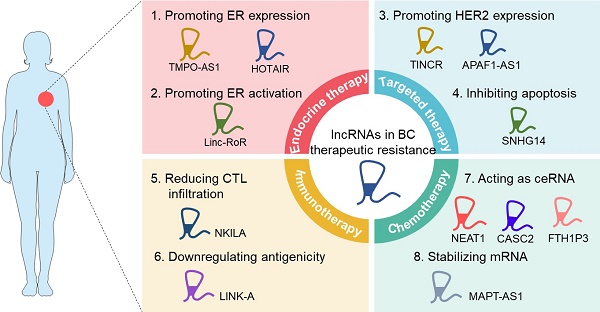
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common female malignancy and the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. In spite of significant advances in clinical management, the mortality of BC continues to increase due to the frequent occurrence of treatment resistance. Intensive studies have been conducted to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying BC therapeutic resistance, including increased drug efflux, altered drug targets, activated bypass signaling pathways, maintenance of cancer stemness, and deregulated immune response. Emerging evidence suggests that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are intimately involved in BC therapy resistance through multiple modes of action. Therefore, an in-depth understanding of the implication of lncRNAs in resistance to clinical therapies may improve the clinical outcome of BC patients. Here, we highlight the role and underlying mechanisms of lncRNAs in regulating BC treatment resistance with an emphasis on lncRNAs-mediated resistance in different clinical scenarios, and discuss the potential of lncRNAs as novel biomarkers or therapeutic targets to improve BC therapy response.
Keywords: Long noncoding RNA, Breast cancer, Drug resistance, Biomarkers, Therapeutic targets
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact