13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(25):7730-7748. doi:10.7150/thno.37306 This issue Cite
Review
The yin and yang of imaging tumor associated macrophages with PET and MRI
1. Department of Bioengineering, Rice University, Houston, TX-77054, United States
2. Werner Siemens Imaging Center, Department of Preclinical Imaging and Radiopharmacy, University Hospital Tuebingen, Eberhard Karls University, Tuebingen, Germany
3. Department of Internal Medicine VIII, University Hospital Tuebingen, Eberhard Karls University, Tuebingen, Germany
4. Department of Radiology, Stanford University, 725 Welch Rd Stanford, CA 94305-5614
‡Equal contribution
*Equal contribution
Abstract
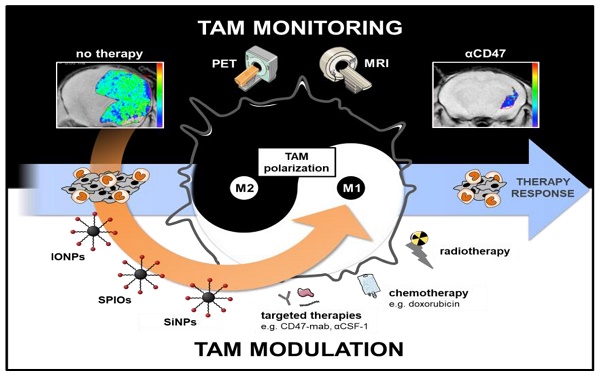
Tumor associated macrophages (TAM) are key players in the cancer microenvironment. Molecular imaging modalities such as MRI and PET can be used to track and monitor TAM dynamics in tumors non-invasively, based on specific uptake and quantification of MRI-detectable nanoparticles or PET-detectable radiotracers. Particular molecular signatures can be leveraged to target anti-inflammatory TAM, which support tumor growth, and pro-inflammatory TAM, which suppress tumor growth. In addition, TAM-directed imaging probes can be designed to include immune modulating properties, thereby leading to combined diagnostic and therapeutic (theranostic) effects. In this review, we will discuss the complementary role of TAM-directed radiotracers and iron oxide nanoparticles for monitoring cancer immunotherapies with PET and MRI technologies. In addition, we will outline how TAM-directed imaging and therapy is interdependent and can be connected towards improved clinical outcomes
Keywords: MRI, PET, Cancer Immunotherapy, Nanoparticles, Radiotracers, Immunotheranostics, Macrophages
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact