13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(22):6665-6675. doi:10.7150/thno.34015 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Luminescent ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes acted as radiosensitizer for pancreatic cancer by enhancing radiation-induced DNA damage
1. School of Chemistry, Biology and Materials Engineering, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Environmental Functional Materials, Suzhou University of Science and Technology, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215009, P. R. China.
2. School of Radiation Medicine and Protection, State Key Laboratory of Radiation Medicine and Protection, Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu 215123, P. R. China.
3. Department of Radiation Physics, Qingdao Central Hospital, Qingdao, Shandong, 266000, P. R. China.
Abstract
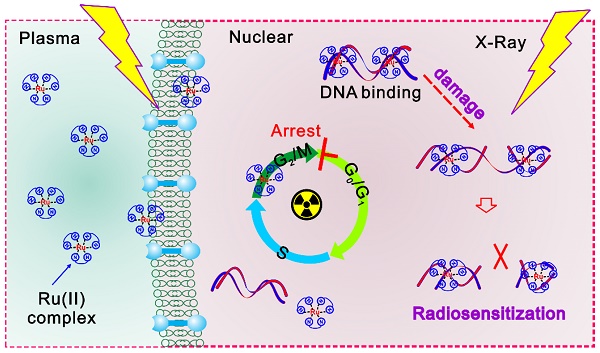
Background: Pancreatic cancer is a highly lethal malignancy which ranks 4th most common cause of cancer death in US and 6th in China. Novel drugs are required to improve the survival and prognosis of patients.
Methods: Ruthenium(II) complexes with variation number of DIP ligand were synthesized and further adopted as radiosensitizer for pancreatic cancer. The influence of ruthenium(II) complexes on cell behaviors and tumor growth were investigated. The DNA binding affinity of ruthenium(II) complexes and plasmid was measured by using agarose gel electrophoresis.
Results: Luminescent ruthenium(II) complex can rapidly enter into cell nuclei and consequently combine with DNA, resulting in the enhanced DNA damage induced by X-ray irradiation. Upon intratumoral injection of ruthenium(II) complex, excellent tumor growth inhibition was accomplished under ionizing radiation of human pancreatic cancer xenograft nude mice.
Conclusions: Taken together, our study suggest that the ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes can effectively enhance radiation-induced DNA damage, which is likely to benefit the imaging-guided cancer radio-chemotherapy.
Keywords: radiosensitizing, ruthenium(II), 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenoline, polypyridyl, pancreatic cancer.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact