13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(22):6468-6484. doi:10.7150/thno.35383 This issue Cite
Research Paper
BCAP31 drives TNBC development by modulating ligand-independent EGFR trafficking and spontaneous EGFR phosphorylation
1. Department of Breast Surgery, Key Laboratory of Breast Cancer in Shanghai, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai 200032, China
2. Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
Abstract
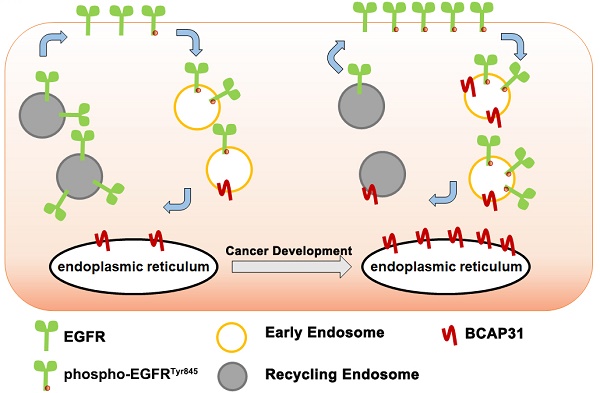
Identification of novel targets for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an urgent task as targeted therapies have increased the lifespans of Oestrogen Receptor +/ Progesterone Receptor + and HER2+ cancer patients.
Methods: genes involved in protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum, which have been reported to be key players in cancer, were used in loss-of-function screening to evaluate the oncogenic roles of these genes to identify candidate target genes in TNBC. In vitro and in vivo function assays as well as clinical prognostic analysis were used to study the oncogenic role of the gene. Molecular and cell based assays were further employed to investigate the mechanisms.
Results: B Cell Receptor Associated Protein 31 (BCAP31), the expression of which is correlated with early recurrence and poor survival among patients, was identified an oncogene in our assay. In vitro studies further suggested that BCAP31 acts as a key oncogene by promoting TNBC development. We also showed that BCAP31 interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and serves as an inhibitor of ligand-independent EGFR recycling, sustaining EGFR autophosphorylation and activation of downstream signalling.
Conclusion: These findings reveal the functional role of BCAP31, an ER-related protein, in EGFR dysregulation and TNBC development.
Keywords: TNBC, BCAP31, EGFR, Cancer Development
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact