13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(22):6263-6273. doi:10.7150/thno.29025 This issue Cite
Research Paper
An enzyme-free biosensor for sensitive detection of Salmonella using curcumin as signal reporter and click chemistry for signal amplification
1. Key Laboratory of Agricultural Information Acquisition Technology, Ministry of Agriculture, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China
2. Key Laboratory on Modern Precision Agriculture System Integration Research, Ministry of Education, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China
3. Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, AR, US
4. College of Veterinary, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
Abstract
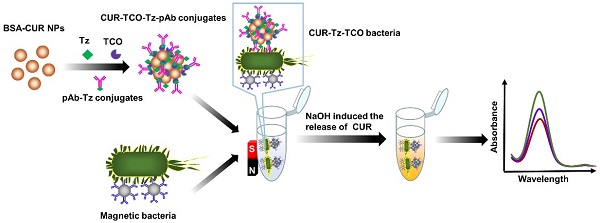
In this study, an enzyme-free biosensor was developed for sensitive and specific detection of Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) using curcumin (CUR) as signal reporter and 1,2,4,5-tetrazine (Tz)-trans-cyclooctene (TCO) click chemistry for signal amplification.
Methods: Nanoparticles composed of CUR and bovine serum albumin (BSA) were formulated and reacted with Tz and TCO to form Tz-TCO-CUR conjugates through Tz-TCO click chemistry. Then, the Tz-TCO-CUR conjugates were functionalized with polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) against S. typhimurium to form CUR-TCO-Tz-pAb conjugates. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) conjugated with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against S. typhimurium through streptavidin-biotin binding were used to specifically and efficiently separate S. typhimurium from the background by magnetic separation. CUR-TCO-Tz-pAb conjugates were reacted with the magnetic bacteria to form CUR-Tz-TCO bacteria. Finally, CUR was released quickly from the CUR-Tz-TCO bacteria in the presence of NaOH, and the color change was measured at the characteristic wavelength of 468 nm for bacteria quantification.
Results: A linear relationship between absorbance at 468 nm and concentration of S. typhimurium from 102 to 106 CFU/mL was found. The lower detection limit was calculated to be as low as 50 CFU/mL and the mean recovery was 107.47% for S. typhimurium in spiked chicken samples.
Conclusion: This biosensor has the potential for practical applications in the detection of foodborne pathogens.
Keywords: enzyme-free biosensor, curcumin, Tz/TCO click reaction, signal amplification, Salmonella typhimurium
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact