13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(5):1350-1360. doi:10.7150/thno.22736 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeting Tumor Hypoxia Using Nanoparticle-engineered CXCR4-overexpressing Adipose-derived Stem Cells
1. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA
2. Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA
Abstract
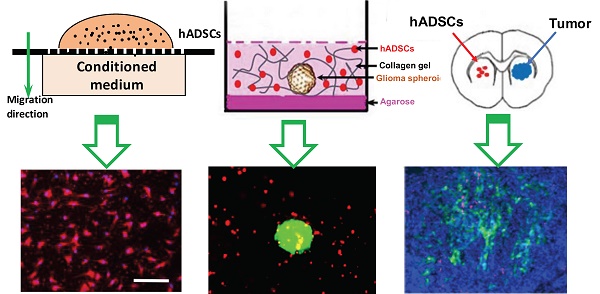
Hypoxia, a hallmark of malignant tumors, often correlates with increasing tumor aggressiveness and poor treatment outcomes. Due to a lack of vasculature, effective drug delivery to hypoxic tumor regions remains challenging. Signaling through the chemokine SDF-1α and its receptor CXCR4 plays a critical role in the homing of stem cells to ischemia for potential use as drug-delivery vehicles. To harness this mechanism for targeting tumor hypoxia, we developed polymeric nanoparticle-induced CXCR4-overexpressing human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs). Using glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) as a model tumor, we evaluated the ability of CXCR4-overexpressing hADSCs to target tumor hypoxia in vitro using a 2D migration assay and a 3D collagen hydrogel model. Compared to untransfected hADSCs, CXCR4-overexpressing hADSCs showed enhanced migration in response to hypoxia and penetrated the hypoxic core within tumor spheres. When injected in the contralateral brain in a mouse intracranial GBM xenograft, CXCR4-overexpressing hADSCs exhibited long-range migration toward GBM and preferentially penetrated the hypoxic tumor core. Intravenous injection also led to effective targeting of tumor hypoxia in a subcutaneous tumor model. Together, these results validate polymeric nanoparticle-induced CXCR4-overexpressing hADSCs as a potent cellular vehicle for targeting tumor hypoxia, which may be broadly useful for enhancing drug delivery to various cancer types.
Keywords: malignant tumors, hypoxia, nanoparticles, adipose-derived stem cells, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), glioblastoma.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact