13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(16):3889-3900. doi:10.7150/thno.20041 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Overexpression of miR-194 Reverses HMGA2-driven Signatures in Colorectal Cancer
1. The Ph.D. Program for Cancer Biology and Drug Discovery, College of Medical Science and Technology, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan;
2. Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kyoto University, Japan.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
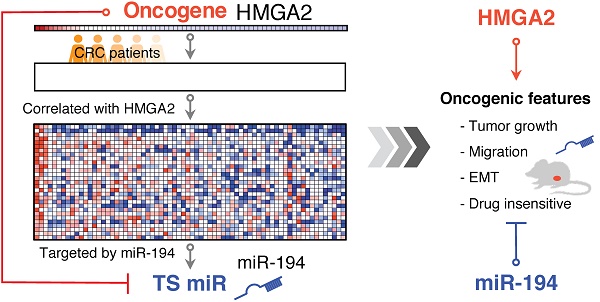
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the leading causes of cancer death worldwide with increasing incidence and mortality in developed countries. Oncogenes and microRNAs regulate key signaling pathways in CRC and are known to be deregulated. Oncogenic transcriptional regulator high-mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) participates in the transformation of several cancers including CRC and exhibits strong correlation with poor prognosis and distal metastasis. Evidence of HMGA2 and its co-regulated miRs contributing to tumor progression remains to be clarified.
Methods: We performed gene-set enrichment analysis on the expression profiles of 70 CRC patients and revealed HMGA2 correlated genes that are targeted by several miRs including miR-194. To eliminate the oncogenic effects in HMGA2-driven CRC, we re-expressed miR-194 and found that miR-194 functions as a tumor suppressor by reducing cell proliferation and tumor growth in vitro and in vivo.
Results: As a direct upstream inhibitory regulator of miR-194, overexpression of HMGA2 reduced miR-194 expression and biological activity, whereas re-expressing miR-194 in cells with high levels of HMGA2 impaired the effects of HMGA2, compromising cell survival, the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process, and drug resistance.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that novel molecular correlations can be discovered by revisiting transcriptome profiles. We uncover that miR-194 is as important as HMGA2, and both coordinately regulate the oncogenesis of CRC with inverted behaviors, revealing alternative molecular therapeutics for CRC patients with high HMGA2 expression.
Keywords: HMGA2, miR-194, gene-set enrichment analysis, colorectal cancer, drug resistance.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact