13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(6):1663-1673. doi:10.7150/thno.17886 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MiR-200c Inhibits the Tumor Progression of Glioma via Targeting Moesin
1. The CAS Key Laboratory of Innate Immunity and Chronic Disease, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at the Microscale, School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230027, China;
2. Innovation Center for Cell Signaling Network;
3. Medical Center, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, P.R. China;
4. Department of Neurosurgery, Anhui Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui 230001, P.R. China;
5. Key Laboratory of Breast Cancer in Shanghai, Cancer Institute, Department of Breast Surgery, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai 200032, China;
6. Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China;
7. AnHui Province Key Laboratory of Brain Function and Brain Disease, Hefei, Anhui 230001, P.R. China.
* These authors contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
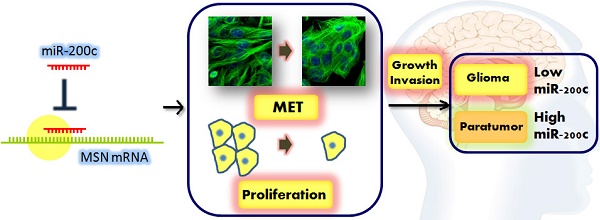
We attempt to demonstrate the regulatory role of miR-200c in glioma progression and its mechanisms behind. Here, we show that miR-200c expression was significantly reduced in the glioma tissues compared to paratumor tissues, especially in malignant glioma. Exogenous overexpression of miR-200c inhibited the proliferation and invasion of glioma cells. In addition, the in vivo mouse xenograft model showed that miR-200c inhibited glioma growth and liver metastasis, which is mainly regulated by targeting moesin (MSN). We demonstrated that the expression of MSN in glioma specimens were negatively correlated with miR-200c expression, and MSN overexpression rescued the phenotype about cell proliferation and invasion induced by miR-200c. Moreover, knockdown of MSN was able to mimic the effects induced by miR-200c in glioma cells. These results indicate that miR-200c plays an important role in the regulation of glioma through targeting MSN.
Keywords: glioma, miR-200c, moesin.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact