13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(5):1373-1388. doi:10.7150/thno.17826 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Simultaneous targeting of CD44 and EpCAM with a bispecific aptamer effectively inhibits intraperitoneal ovarian cancer growth
1. Center for Biotechnology and Genomic Medicine, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta University, Augusta, GA 30912, USA;
2. Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL 32610, USA.
3. Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, The second hospital of Jilin University, Jinlin University, Changchun, 130041, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
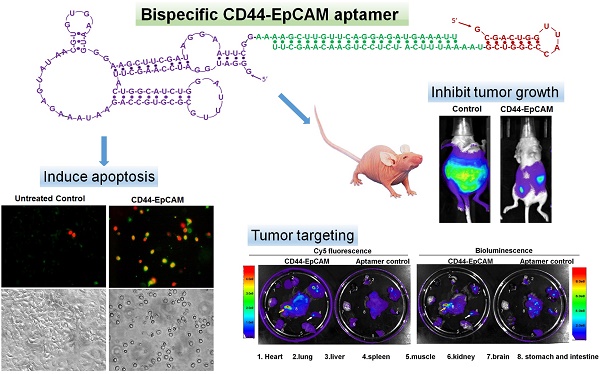
CD44 and EpCAM play crucial roles in intraperitoneal ovarian cancer development. In this study, we developed an RNA-based bispecific CD44-EpCAM aptamer that is capable of blocking CD44 and EpCAM simultaneously by fusing single CD44 and EpCAM aptamers with a double stranded RNA adaptor. With the aid of a panel of ovarian cancer cell lines, we found that bispecific CD44-EpCAM aptamer was much more effective than either single CD44 or EpCAM aptamer in the ability to inhibit cell growth and to induce apoptosis. When these aptamers were tested in intraperitoneal ovarian cancer xenograft model, bispecific CD44-EpCAM aptamer suppressed intraperitoneal tumor outgrowth much more significantly than single CD44 and EpCAM aptamer either alone or in combination. The enhanced efficacy of bispecific CD44-EpCAM aptamer is most likely to be attributed to its increased circulation time over the single aptamers. Moreover, we showed that bispecific CD44-EpCAM aptamer exhibited no toxicity to the host and was unable to trigger innate immunogenicity. Our study suggests that bispecific CD44-EpCAM aptamer may represent a promising therapeutic agent against advanced ovarian cancer.
Keywords: CD44, EpCAM, aptamer, intraperitoneal tumor growth, bispecific molecule.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact