13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(9):3565-3582. doi:10.7150/thno.92119 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A novel selenium analog of HDACi-based twin drug induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via CDC25A to improve prostate cancer therapy
1. Department of Molecular Pharmacology, School of Medicine; College of Pharmacy, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Drug Research, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China.
2. Institute of Digestive Disease, Shengli Oilfield Central Hospital, Dongying 257000, China.
3. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Branch of Tianjin Third Central Hospital, Tianjin 300250, China.
4. The First Department of Critical Care Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University, Shihezi, 832003, China.
5. Tianjin Key Laboratory of General Surgery in Construction, Tianjin Union Medical Center, Tianjin 300122, China.
# Zhiyong Shi and Miaomiao Liu contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
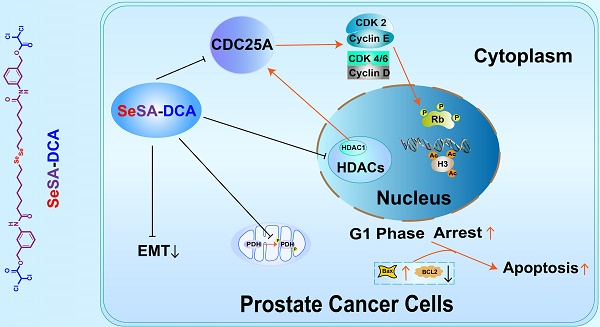
Cancer therapy has moved from single agents to more mechanism-based targeted approaches. In recent years, the combination of HDAC inhibitors and other anticancer chemicals has produced exciting progress in cancer treatment. Herein, we developed a novel prodrug via the ligation of dichloroacetate to selenium-containing potent HDAC inhibitors. The effect and mechanism of this compound in the treatment of prostate cancer were also studied.
Methods: The concerned prodrug SeSA-DCA was designed and synthesized under mild conditions. This compound's preclinical studies, including the pharmacokinetics, cell toxicity, and anti-tumor effect on prostate cancer cell lines, were thoroughly investigated, and its possible synergistic mechanism was also explored and discussed.
Results: SeSA-DCA showed good stability in physiological conditions and could be rapidly decomposed into DCA and selenium analog of SAHA (SeSAHA) in the tumor microenvironment. CCK-8 experiments identified that SeSA-DCA could effectively inhibit the proliferation of a variety of tumor cell lines, especially in prostate cancer. In further studies, we found that SeSA-DCA could also inhibit the metastasis of prostate cancer cell lines and promote cell apoptosis. At the animal level, oral administration of SeSA-DCA led to significant tumor regression without obvious toxicity. Moreover, as a bimolecular coupling compound, SeSA-DCA exhibited vastly superior efficacy than the mixture with equimolar SeSAHA and DCA both in vitro and in vivo. Our findings provide an important theoretical basis for clinical prostate cancer treatment.
Conclusions: Our in vivo and in vitro results showed that SeSA-DCA is a highly effective anti-tumor compound for PCa. It can effectively induce cell cycle arrest and growth suppression and inhibit the migration and metastasis of PCa cell lines compared with monotherapy. SeSA-DCA's ability to decrease the growth of xenografts is a little better than that of docetaxel without any apparent signs of toxicity. Our findings provide an important theoretical basis for clinical prostate cancer treatment.
Keywords: HDAC inhibitors, SAHA selenium analogs, synergistic therapy, PDH, CDC25A
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact