13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(8):3358-3384. doi:10.7150/thno.95953 This issue Cite
Review
Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the therapeutic intervention of Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and stroke
1. National Vaccine Serum Institute (NVSI), China National Biotech Group (CNBG), Sinopharm Group, No. 38 Jing Hai Second Road, Beijing 101111, China.
2. Capital Medical University, 10 Xitoutiao, Youanmenwai Street, Beijing 100069, China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Biochemical Engineering, Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China.
Abstract
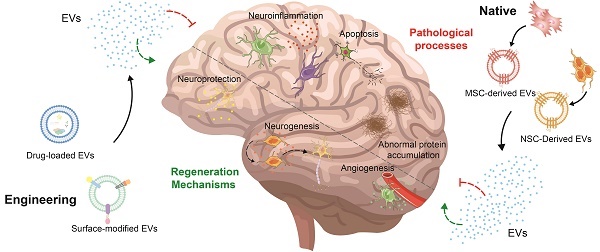
With the increase in the aging population, the occurrence of neurological disorders is rising. Recently, stem cell therapy has garnered attention due to its convenient sourcing, minimal invasiveness, and capacity for directed differentiation. However, there are some disadvantages, such as poor quality control, safety assessments, and ethical and logistical issues. Consequently, scientists have started to shift their attention from stem cells to extracellular vesicles due to their similar structures and properties. Beyond these parallels, extracellular vesicles can enhance biocompatibility, facilitate easy traversal of barriers, and minimize side effects. Furthermore, stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles can be engineered to load drugs and modify surfaces to enhance treatment outcomes. In this review, we summarize the functions of native stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles, subsequently review the strategies for the engineering of stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles and their applications in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and stroke, and discuss the challenges and solutions associated with the clinical translation of stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles.
Keywords: stem cell, extracellular vesicle, neurological disease, drug delivery, clinical translation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact