13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(1):420-435. doi:10.7150/thno.89105 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Klotho-derived peptide 1 inhibits cellular senescence in the fibrotic kidney by restoring Klotho expression via posttranscriptional regulation
1. Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, National Clinical Research Center of Kidney Disease, Guangdong Provincial Institute of Nephrology, Guangzhou, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
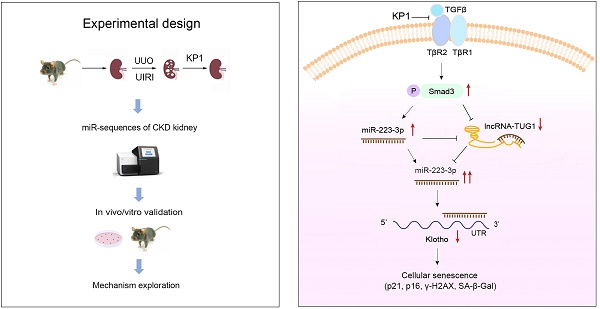
Background: Klotho deficiency is a common feature of premature aging and chronic kidney disease (CKD). As such, restoring Klotho expression could be a logic strategy for protecting against various nephropathies. In this study, we demonstrate that KP1, a Klotho-derived peptide, inhibits cellular senescence by restoring endogenous Klotho expression.
Methods: The effects of KP1 on cellular senescence and Klotho expression were assessed in mouse models of CKD. RNA-sequencing was employed to identify the microRNA involved in regulating Klotho by KP1. Gain- or loss-of-function approaches were used to assess the role of miR-223-3p and IncRNA-TUG1 in regulating Klotho and cellular senescence.
Results: KP1 inhibited senescence markers p21, p16 and γ-H2AX in tubular epithelial cells of diseased kidneys, which was associated with its restoration of Klotho expression at the posttranscriptional level. Profiling of kidney microRNAs by RNA sequencing identified miR-223-3p that bound to Klotho mRNA and inhibited its protein expression. Overexpression of miR-223-3p inhibited Klotho and induced p21, p16 and γ-H2AX, which were negated by KP1. Conversely, inhibition of miR-223-3p restored Klotho expression, inhibited cellular senescence. Furthermore, miR-223-3p interacted with lncRNA-TUG1 and inhibited its expression. Knockdown of lncRNA-TUG1 increased miR-223-3p, aggravated Klotho loss and worsened cellular senescence, whereas KP1 mitigated all these changes.
Conclusion: These studies demonstrate that KP1 inhibits cellular senescence and induces Klotho expression via posttranscriptional regulation mediated by miR-223-3p and lncRNA-TUG1. By restoring endogenous Klotho, KP1 elicits a broad spectrum of protective actions and could serve as a promising therapeutic agent for fibrotic kidney disorders.
Keywords: Klotho, cellular senescence, miRNA-223-3p, lncRNA-TUG1, kidney fibrosis, chronic kidney disease
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact